Market Summary
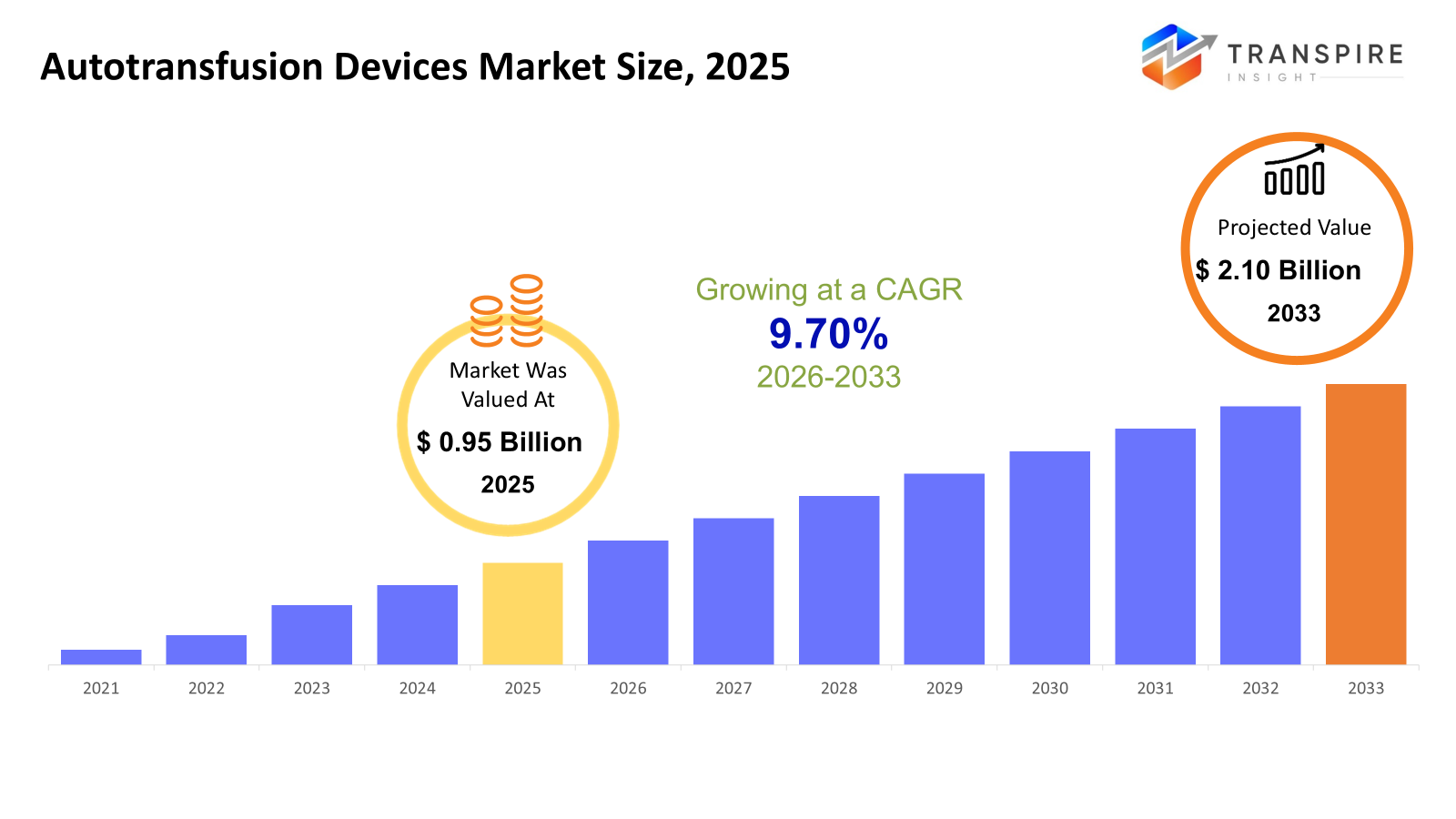
The global Autotransfusion Devices market size was valued at USD 0.95 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2.10 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.70% from 2026 to 2033. More people needing surgery helps explain why demand for autotransfusion equipment keeps climbing worldwide. Awareness around smarter ways to handle a patient's own blood plays a role, too. Hospitals now look more closely at self-blood recovery because donated supplies run short more often. Risks tied to traditional transfusions, like infections or bad reactions, push institutions toward safer alternatives. Devices that clean and recycle blood during operations gain favor as technology evolves. Modern machines using spin cycles work faster, with fewer errors. Better performance makes medical teams more likely to rely on them day after day.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 0.95 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 2.10 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 9.70%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- The North American market share is estimated to be approximately 40% in 2026. Across North America, advanced surgical practices help drive demand, since hospitals there rely heavily on reinfusing patients’ own blood. Complex operations often include this method, which supports recovery while reducing donor dependence.
- The United States, fueled by widespread use of patient blood management, is experiencing growth surges across the region. Surgical methods here push forward, not held back by old habits.
- Hospital upgrades push growth across Asia Pacific. Surgical cases climb higher each year there. Money flows into health systems, fueling expansion. Rising demand meets better facilities, slowly taking shape.
- Intraoperative Autotransfusion Systems share approximately 30% in 2026. Most operating rooms rely on Intraoperative Autotransfusion Systems during complex procedures where bleeding is heavy. These devices see widespread use because they return lost blood to the patient quickly. Their role grows as more hospitals prioritize efficient surgical support tools. Performance under pressure makes them a go-to choice in critical moments. Surgeons favor them especially when managing large volume shifts in real time.
- Out of the box, autotransfusion tech takes top spot; hospitals lean toward automation when it comes to recovering blood faster and cleaner. Efficiency sneaks in quietly, yet makes a difference; safety rides alongside without drawing attention. Machines handle the work once done by hand, shifting how clinics operate behind closed doors. Preference grows not from hype but steady performance seen over time in real rooms.
- Spinning systems lead because they clean blood better plus deliver trusted results in real medical settings.
- Most care centers see heavy use because of countless operations plus strong medical setups.
During surgery or afterward, machines gather a person's blood, clean it up, and then return it to their body, cutting down how much donated blood gets used. Because of these tools, chances drop for problems tied to someone else’s blood, like sicknesses or immune system flare-ups. With medical centers aiming for cleaner, smoother operations, gear that recycles a patient’s own blood now fits right into today’s surgical spaces.
During operations where bleeding is heavy, like heart, bone, or injury-related surgeries, machines that recycle a patient's own blood see frequent use. After surgery, similar devices collect lost blood through drainage tubes, helping patients heal while lowering the need for donor blood. Ongoing sales of disposable parts and tools keep this area active, since each procedure requires fresh supplies to run properly.
Now comes a wave of new tools changing how clinics handle blood during surgery. Machines that spin fast take over messy handwork, cutting errors along the way. Instead of relying on old routines, hospitals lean into systems that clean blood more quickly than before. Safety climbs when human steps shrink in delicate processes. Devices behave better under pressure, fitting smoothly into tense operating rooms. Surgeons notice fewer hiccups when tech blends quietly into their rhythm. Less fuss means teams trust these helpers more each time they switch them on. Progress hides inside quiet upgrades, no fanfare, just steady gains where lives hang in balance.
Now, shaping things more than ever, shifting medical habits are focused on saving money, protecting patients, and leaving less waste. Devices that recycle a person's own blood see wider use in hospitals and surgery hubs, slipping into routine practice bit by bit. Driven not just by results but by how smoothly they fit into real-world demands, these tools quietly redefine what careful surgery looks like today.
Autotransfusion Devices Market Segmentation
By Product Type
- Intraoperative Autotransfusion Systems
Blood saved mid-surgery flows back into the body, skipping outside sources. Mid-procedure recycling pulls lost volume and returns it clean. This loop cuts the need for someone else’s supply. Machine-assisted recovery happens while the operation moves forward. A person's own reserve becomes the backup when bleeding occurs.
- Postoperative Autotransfusion Systems
Recover blood from surgical drains after procedures for reinfusion and blood conservation.
- Consumables and Accessories
Tubing shows up first, then filters join in. Reservoirs come along afterward, doing their part. Anticoagulants tag along last, making sure things stay smooth.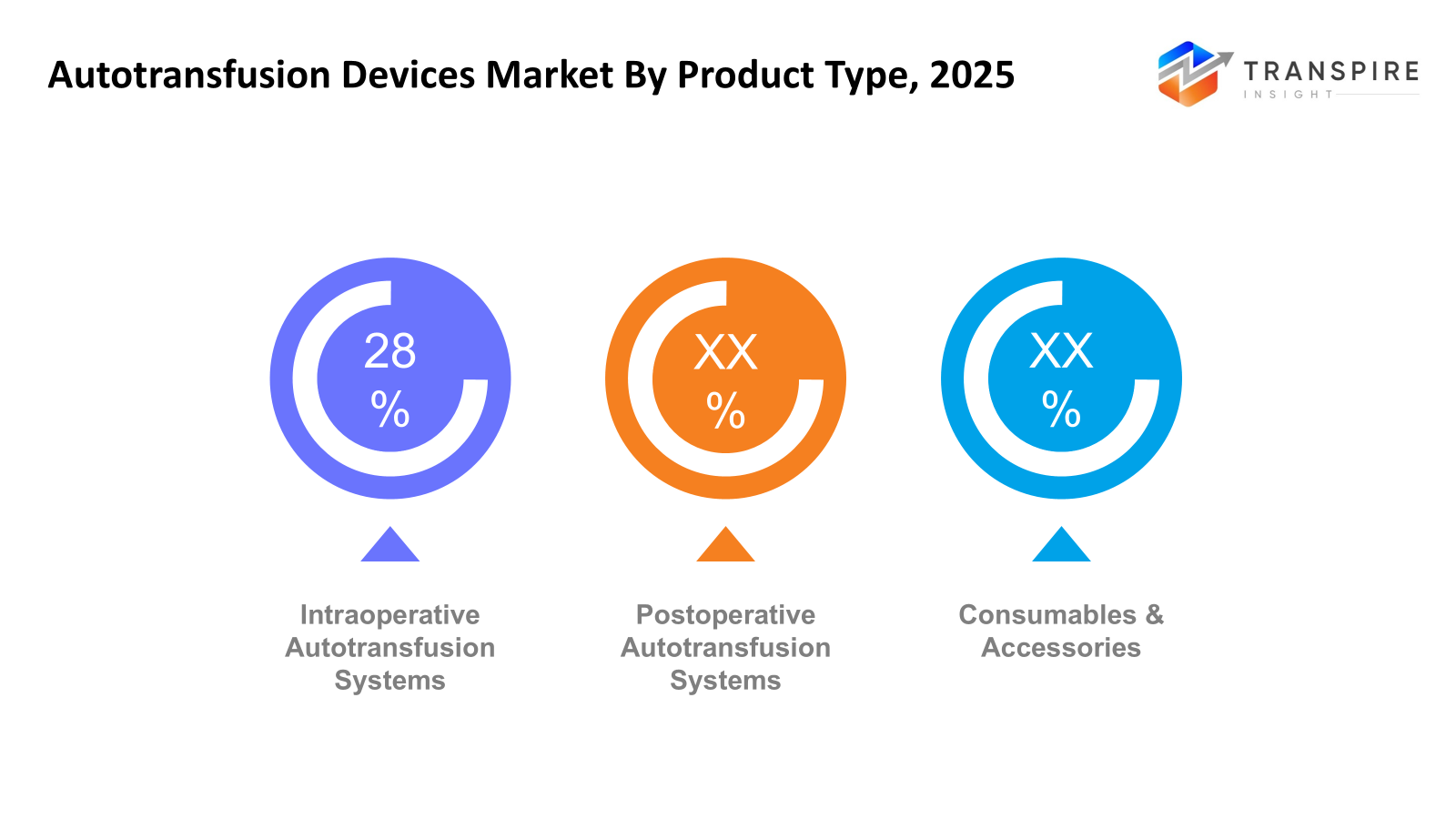
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Mode of Operation
- Automatic Autotransfusion Devices
Built-in blood recovery tools run on their own, needing less hands-on work. These units operate without constant control, making them more dependable. Efficiency climbs because steps happen in sequence, without delays. Safety improves since fewer human actions are involved. Machines handle the collection smoothly, cutting chances for mistakes. Less touching by staff means cleaner processes overall.
- Semi-Automatic Autotransfusion Devices
Machines that recycle blood need some human help; these models cost less than fully automatic ones because they do part of the work themselves, but still depend on someone watching closely. Their simpler design keeps prices down compared to systems handling everything alone.
By Technology
- Centrifugation-Based Systems
Spinning machines pull red blood cells apart by force, then rinse them clean. These setups show up often in busy operating rooms where lots of procedures happen.
- Filtration-Based Systems
Starting with a filter, these systems trap unwanted particles. Often found where tasks are basic or output is small. Using physical barriers helps clean liquids step by step. Common in setups that do not need heavy processing. Found across labs when volume stays low.
By End-Users
- Hospitals
Because surgeries happen so often, hospitals rely heavily on these tools. Advanced equipment sits ready inside their operating spaces, making adoption natural.
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Fueled by a rise in outpatient care, ambulatory surgical centers see growing use. Minimally invasive techniques pull more patients toward these settings. Elective surgeries play a role, too, shifting away from traditional hospitals. Cost efficiency helps, yet convenience matters just as much. Even recovery times shape where people choose to go. These clinics adapt quickly, matching patient demand with speed.
- Specialty Clinics
Some clinics focus on heart, bone, or injury care, and these often apply autotransfusion during specific operations. Procedures there rely on reusing a patient’s own blood when needed most. A heartbeat, a broken limb, or serious wounds, each case might involve this method. These centers choose it because it fits their precise medical demands.
- Others
Emergency care units fall under this category. Military hospitals are included, too. Research centers make up part of it as well.
Regional Insights
From operating rooms in well-equipped hospitals, autotransfusion tools are now common, where managing a patient’s own blood matters most during surgery. Leading the way, North America uses these systems heavily because its medical centers run on modern setups, understand complications tied to donor blood, while relying more on machines that reclaim blood during intricate procedures. Right behind, Europe advances similar use backed by clear medical protocols, older citizen groups needing care, along with a growing push to limit outside blood sources by giving patients back their own.
A surge in operations fuels demand across the Asia Pacific, where clinics update facilities and prioritize efficient blood use. Modernizing hospitals in nations like China, India, and Japan now routinely employ autotransfusion tools during heart, joint, and injury procedures. Training surgeons boosts confidence in these methods, while wider medical access expands their reach. Growth gains momentum as resources align with evolving clinical needs. Equipment usage climbs steadily alongside system upgrades and knowledge sharing.
Across Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, the use of autotransfusion tech creeps forward slowly. Boosted by fresh funding for medical centers, growth doesn’t rely only on public systems - private clinics play a part too. Patient well-being gains more attention now, which shifts how surgeries are handled. Cost matters more these days, nudging teams toward smarter tools. Even though usage lags behind wealthier nations, knowledge spreads wider than before. Equipment like this finds firmer footing where roads, power, and training improve. Steady progress takes root, step by uneven step.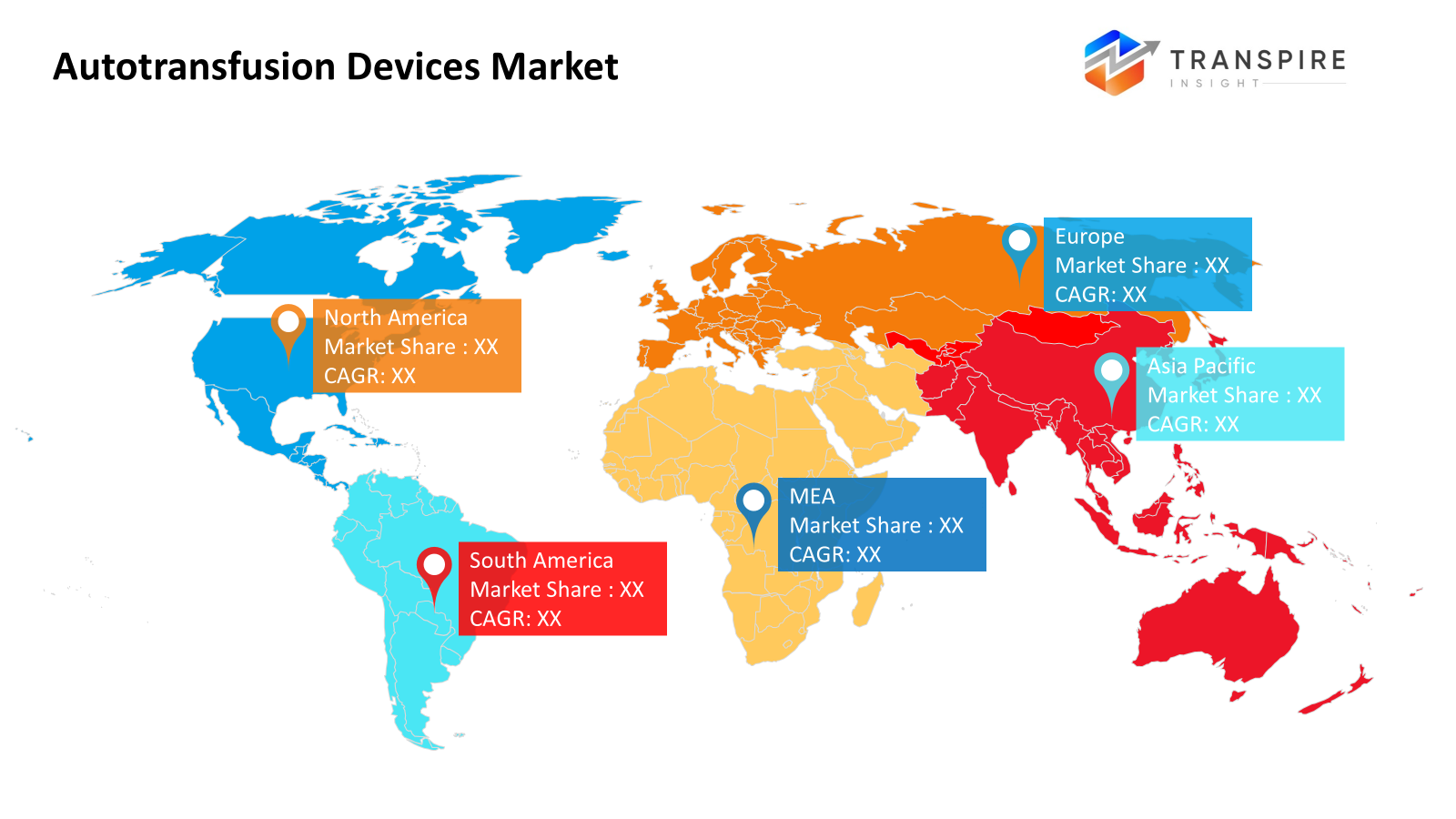
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- August 12, 2025 – Stago UK introduced a novel platelet-retrieving device.
(Source:https://www.pathologyinpractice.com/story/45656/stago-uk-introduces-novel-platelet-retrieving-device
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 0.95 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 1.10 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 2.10 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 9.70% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Haemonetics Corporation, Fresenius Kabi, Medtronic plc, LivaNova PLC, Terumo Corporation, B. Braun Melsungen AG, Getinge AB, Beijing ZKSK Technology Co. Ltd, Redax, Braile Biomedica, Haematonics Corporation, Teleflex Incorporated, LivaNova Inc., and BD Company. |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Product Type (Intraoperative Autotransfusion Systems, Postoperative Autotransfusion Systems, Consumables & Accessories), By Mode of Operation (Automatic Autotransfusion Devices, Semi-Automatic), By Technology (Centrifugation-Based Systems, Filtration-Based Systems), By End-Users (Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Specialty Clinics, Others) |
Key Autotransfusion Devices Company Insights
One name stands out when it comes to machines that recycle blood during surgery: Haemonetics. Not just known, but built around smart ways to save and reuse blood safely. Machines that work fast, need less hand control, yet deliver steady results in tough operations. Innovation does not stall because money keeps flowing into research. Working side by side with medical centers helps shape the tools surgeons actually use. New versions arrive often, thanks to real feedback from clinics worldwide. Growth spreads quietly, powered by trust and repeated upgrades.
Key Autotransfusion Devices Companies:
- Haemonetics Corporation
- Fresenius Kabi
- Medtronic plc
- LivaNova PLC
- Terumo Corporation
- Braun Melsungen AG
- Getinge AB
- Beijing ZKSK Technology Co. Ltd
- Redax
- Braile Biomedica
- Haematonics Corporation
- Teleflex Incorporated
- BD Company
Global Autotransfusion Devices Market Report Segmentation
By Product Type
- Intraoperative Autotransfusion Systems
- Postoperative Autotransfusion Systems
- Consumables & Accessories
By Mode of Operation
- Automatic Autotransfusion Devices
- Semi-Automatic
By Technology
- Centrifugation-Based Systems
- Filtration-Based Systems
By End-Users
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Specialty Clinics
- Others
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa










.jpg)









 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





