Market Summary
The global Surgical Robots market size was valued at USD 13.69 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 40.92 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 14.67% from 2026 to 2033. This strong growth is driven by the rising adoption of minimally invasive surgical procedures, which offer reduced recovery time, lower complication rates, and improved patient outcomes.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 13.69 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 40.92 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 14.67%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market

To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- North America market share estimated to be approximately 62% in 2026. Across North America, hospitals use robotic tools more than anywhere else. This happens because medical care there is highly developed. Insurance often covers these procedures. Many surgeries take place each year in fields like urinary health and abdominal operations. Equipment adoption grows where systems make it easier to apply.
- They are already common across the United States clinics, due to steady approvals from regulators. Big city centers embraced them first, yet smaller local hospitals followed close behind. This country still leads the region when it comes to using such systems at scale. Progress keeps moving forward, one hospital at a time.
- In the Asia Pacific, down under and across, medical upgrades push growth, and more operations happen now. New tools arrive through state-backed plans. Hospitals stretch wider and busier every year. Rising numbers head into the surgery rooms. Progress hums strongest here, where care systems grow fast
- Autonomous Surgical Robots share approximately 43% in 2026. Machines that operate on their own inside operating rooms now move forward fast, smart software plus sharper controls allow tighter accuracy during common surgeries. These tools adapt well when tasks stay predictable and follow set patterns.
- Minimally invasive robotic surgery pulls ahead with fewer issues after procedures, quicker bounce-back periods, and better results in patient care when set beside traditional open methods. That’s where most interest lies these days.
- Even though many areas use robotics, general surgery leads because it covers a wide range of operations. More hospitals now choose robots for tough tasks such as fixing hernias or working on the colon. This shift helps explain why this field stays ahead. Still, progress in other specialties continues at its own pace.
- Hospitals lead the way when it comes to using surgical robots, handling high patient numbers while already equipped with both funds and facilities. Their setup makes adopting complex systems far more practical than elsewhere.
Not long ago, robots in surgery were rare. Now they are showing up more often as hospitals look for better accuracy during operations. Some run on their own, others need human help, while some just assist without taking control. These tools get used everywhere, fixing joints, heart issues, bladder problems, women's health, and even niche surgeries. Smarter software that sees what it’s doing, learns from data, almost like a co-pilot for doctors. Progress keeps rolling because machines now understand images, adapt mid-operation, and follow complex plans. Growth isn’t slowing down any time soon.
A growing number choose operations that don’t require big cuts, simply because getting back to life matters more now. Clinics are not buying robots just to keep up. They see crowded waiting rooms when they offer something seen as safer, smarter. Even small surgical hubs are shifting gears, pulled by what patients start asking for after hearing stories from friends or doctors. Recovery time used to be measured in weeks; today, many expect it in days, and tools that help achieve that gain quick trust. Behind every machine purchase lies a mix of pressure, possibility, and real shifts in what counts as acceptable care.
Robotic arms keep getting better, due to steady upgrades in design and function. Endoscopic tools now allow deeper access without needing large incisions. Control panels have evolved alongside smarter software that adapts during operations. Machines powered by artificial intelligence help guide decisions mid-surgery. Clearer imaging gives doctors real-time views they could not see before. Navigation aids act like GPS for delicate moves inside the body. Precision climbs when these elements work together behind the scenes.
Fewer surgeons struggle through long procedures now that machines help with tricky cuts. Machines learn faster because data flows straight into their planning steps. Some hospitals redesign rooms just to fit these tools better. Growth keeps coming as clinics see fewer delays after switching to automated helpers. Money follows where results show up first, especially when recovery speeds improve. New designs arrive yearly thanks to real-world feedback shaping upgrades.
Surgical Robots Market Segmentation
By Type
- Semi-Autonomous Surgical Robots
Robots that help during surgery are being used more often because they mix machine support with human guidance. This teamwork allows for greater accuracy when operating.
- Autonomous Surgical Robots
Far beyond remote control, machines now learn precise motions needed for routine operations. These systems follow strict patterns, reducing the need for hands-on guidance. Step by step, they handle tasks once done only by surgeons. Little by little, automation takes root in controlled medical environments.
- Non-Autonomous Surgical Robots
Far from independent, these robots still play a major role simply because surgeons operate them directly. Their presence sticks around by fitting neatly into routines already in place across operating rooms. Control stays firmly in human hands, yet their contribution remains solid within familiar processes.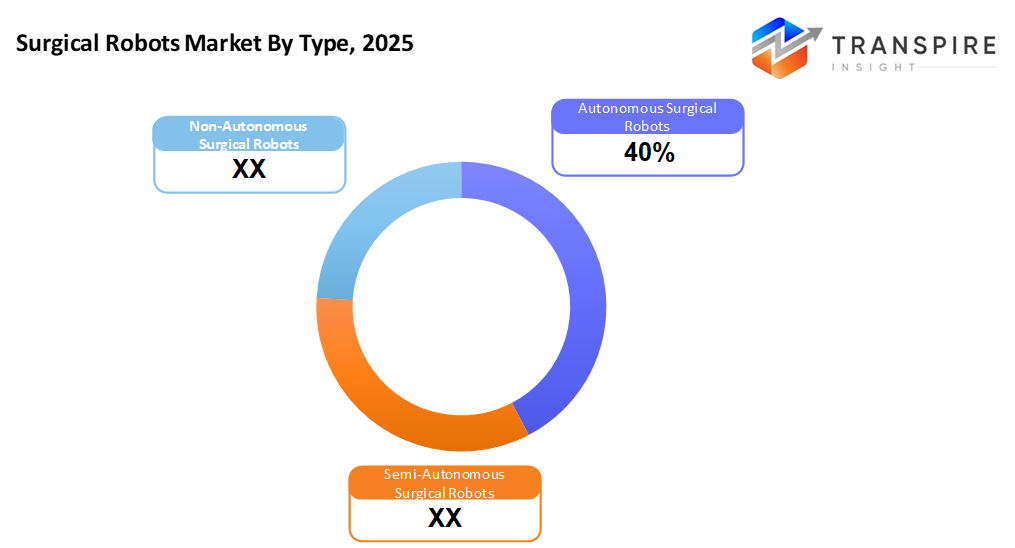
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Mode of Operation
- Open Robotic Surgery
With open techniques, robotic surgery tackles tough operations where full access matters. This approach brings together machine accuracy and classic hands-on methods. It works when intricate tasks need a wider view. Precision tools help surgeons operate through larger openings. The method suits cases that demand both reach and control. Using robotics here means better handling during demanding steps.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
Surgery using robots causes less harm to patients, so people want it more. Shorter healing periods help too, not just better results in clinics. Machines move gently inside the body. This change came slowly, but it matters a lot.
- Laparoscopic Robotic Surgery
Surgery using robotic tools works well for the belly and lower body areas. These machines help doctors move with more precision than standard keyhole methods. Clearer views of the area also come from the technology used. Some find it easier to operate this way.
By Application
- General Surgery
Fine control matters most when tools move inside the body during common operations. Where hands can tremble, machines hold steady without fatigue. Mistakes happen less often once robots take part in cutting and stitching tasks. Most hospitals now test these systems before scaling up usage across departments.
- Orthopedic Surgery
Robotic tools now help fix joints with better accuracy. This kind of surgery is expanding quickly. Improved positioning during procedures makes a difference. Machines assist doctors in aligning bones more carefully. Growth comes from these precise methods. Fewer errors happen when technology guides the work. Results improve when movements are controlled. Surgeons rely on automation for consistency. Better outcomes drive interest in these techniques. Progress shows in recovery times, too.
- Cardiovascular Surgery
Surgery on the heart sees more use of robots; these machines help doctors handle tough procedures with greater precision. Less cutting means less harm, making recovery smoother. Tools guided by robotic arms move where hands struggle to reach. Patients benefit quietly, without fanfare, with improved outcomes over time.
- Urological Surgery
Few areas see such steady demand as surgery focused on urinary health. Precision matters most when dealing with organs like the prostate or kidneys. Procedures here often involve careful cutting work, done slowly and deliberately. Much of what drives advancement comes straight from real operating room needs.
- Gynecological Surgery
Fresh advances in gynecological surgery emerge through robotic tools that allow smaller incisions during hysterectomy work. These methods spread fast because they ease recovery without major cuts. Machines assist precision tasks once done only by open techniques. Movement toward less invasive paths grows steady. Fewer scars follow these updated approaches. Doctors adapt steadily to electronic helpers in delicate areas.
- Others
Fine motor precision gets a boost in fields like ear-nose-throat work, brain surgery, and child care. Robotic tools help here. Surgeons' tiredness drops when machines assist during long procedures in these areas.
By End-Users
- Hospital
Hospitals stand out as the biggest users. Their high number of surgeries drives demand. Money flows into cutting-edge robots because facilities can afford them. Large operations need precise tools regularly.
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Outpatient surgeries are on the rise as more people choose less invasive options. These centers see higher use because patients prefer quick recovery times. Medical advances make it possible to avoid overnight stays. Comfort matters just as much as convenience here. Efficiency pulls both doctors and patients toward these clinics. New techniques continue shaping how care gets delivered outside hospitals.
- Specialty Clinics
Beyond general hospitals, specialty clinics are leaning into advanced gear tailored to specific surgeries. This shift aims at sharper results. Tools designed for particular operations now see wider adoption where accuracy matters most. Patient recovery times tend to shorten when equipment matches the exact needs of a procedure. Focused environments adopt these instruments to stay aligned with evolving techniques.
Regional Insights
Right now, North America holds the biggest share of the surgical robot market, mainly due to well-developed medical facilities and quick uptake of new tech. Leading that region is the United States, where hospitals started using robotic surgery systems years ago. Regulatory backing from the FDA keeps fueling growth there, making room for newer models to enter clinical practice. Over in Europe, nations such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom show rising interest in less invasive operations, pushing demand upward. There, modern health networks help integrate robotics into routine care. Together, these regions form the core base for current robotic surgery usage.
Growth surges across the Asia Pacific, driven by more surgeries taking place every year. Healthcare systems keep expanding, creating room for advanced tools to enter operating rooms. Robotic surgery tech draws greater funding, especially in nations like China, Japan, and India. Public hospitals adopt these machines just as fast as private ones do. Government programs help speed things up, while people earn more and can afford better care. A huge number of patients live here, adding pressure on medical services to improve. Awareness spreads about less invasive methods that get people back on their feet sooner. Shorter time in hospital becomes a real possibility due to precise robotic assistance. Recovery improves without needing long stays under observation.
Across Latin America, progress moves step by step as health services update and hospitals grow. Brazil stands out, bringing in robotic surgery through fresh funding and partnerships. Mexico follows closely, building similar pathways into advanced medical tech. Not far behind, cities in the Middle East and parts of Africa turn attention to precision tools in operating rooms. Major hubs choose costly robotic setups, aiming for better results in complex procedures. Specialized clinics and large treatment facilities lead this shift. Growth stays steady rather than fast, yet signs point upward where medicine meets innovation.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- November 6, 2025 – SS Innovation launched MantrAsana, worlds first portable robotic surgery system.
- September 14, 2025 – Delhi AIIMS launched Da Vinci Surgical Robots to train doctors.
- April 14, 2025 – Johnson & Johnson MedTech announced completion of first classes with Ottava™ robotic surgical system.
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 13.69 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 15.70 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 40.92 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 14.67% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Intuitive Surgical Inc., Medtronic Plc, Stryker Corporation, Zimmer Biomet, CMR Surgical, Renishaw Plc, Smith and Nephew, Think Surgical Inc., Moon Surgical, Meril Life Sciences, MicroPort, SS Innovations, Meril Life Science, Vicarious Surgical, and Momentis Surgical. |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Type (Semi-Autonomous Surgical Robots, Autonomous Surgical Robots, Non-Autonomous Surgical Robots) By Mode of Operation(Open Robotic Surgery, Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery, Laparoscopic Robotic Surgery) By Application (General Surgery, Orthopedic Surgery, Cardiovascular Surgery, Urological Surgery, Gynecological Surgery, Others) By End-Users (Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Specialty Clinics) |
Key Surgical Robots Company Insights
Intuitive Surgical, Inc. is the global leader in the surgical robots market, best known for its da Vinci Surgical System, which is widely used across urology, general surgery, gynecology, and cardiothoracic procedures. The company benefits from a large installed base, strong recurring revenue from instruments and services, and continuous innovation in robotic-assisted surgery. Intuitive Surgical focuses heavily on improving precision, visualization, and surgeon ergonomics through advanced robotics and software integration. Its strong clinical evidence base and extensive surgeon training programs reinforce its dominant market position.
Key Surgical Robots Companies:
- Intuitive Surgical Inc.
- Medtronic Plc
- Stryker Corporation
- Zimmer Biomet
- CMR Surgical
- Renishaw Plc
- Smith and Nephew
- Think Surgical Inc.
- Moon Surgical
- Meril Life Sciences
- MicroPort
- SS Innovations
- Meril Life Science
- Vicarious Surgical
- Momentis Surgical.
Global Surgical Robots Market Report Segmentation
By Type
- Semi-Autonomous Surgical Robots
- Autonomous Surgical Robots
- Non-Autonomous Surgical Robots
By Mode of Operation
- Open Robotic Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery
- Laparoscopic Robotic Surgery
By Application
- General Surgery
- Orthopedic Surgery
- Cardiovascular Surgery
- Urological Surgery
- Gynecological Surgery
- Others
By End-Users
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Specialty Clinics
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa










.jpg)









 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





