Market Summary
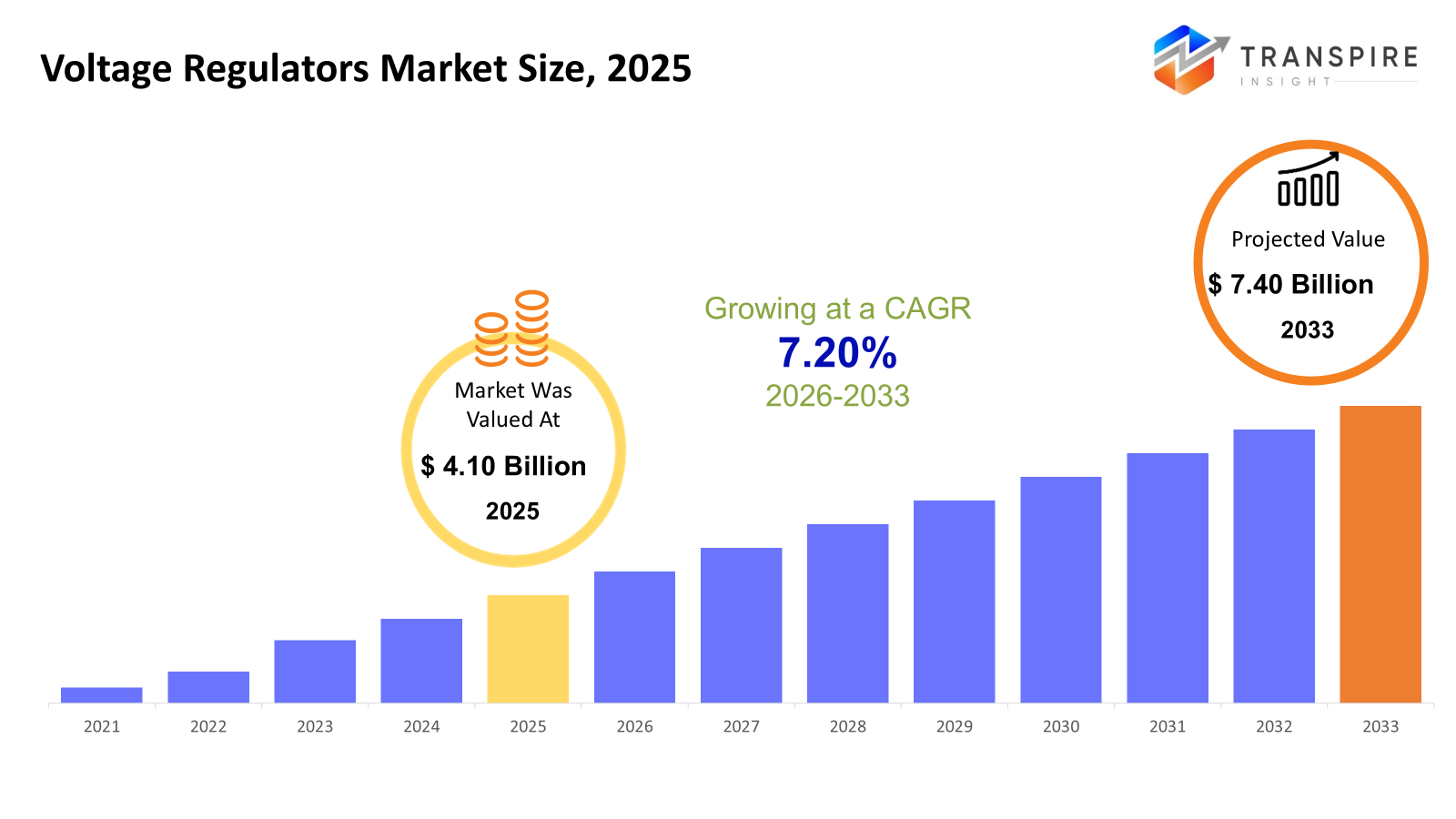
The global Voltage Regulator market size was valued at USD 4.10 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 7.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.20% from 2026 to 2033. A surge in global electricity usage pushes the need for steady power, especially in homes, businesses, and factories. Because more gadgets and automated setups are in play, precise voltage management becomes essential. On top of that, cleaner energy sources entering the mix add pressure to keep electrical flow consistent. Upgrades to how power moves across regions create fresh openings for these systems. Investment in smarter grids adds momentum, shaping how the sector evolves ahead.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 4.10 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 7.40 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 7.20%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- The North American market share is estimated to be approximately 35% in 2026. Fresh funding flows into North America's grid systems, pushing modern control gear into wider use. Upgrades to electricity networks there now rely heavily on smarter regulation tools. New tech steps in where older setups once struggled. Infrastructure changes across the region create a steady need for precision devices. Equipment with sharper response patterns finds growing space in these projects. Investment waves open doors for next-gen solutions. Grid improvements become a stage for innovation.
- Strong factories keep the region moving forward in the United States, while wind and solar find their way into daily use. Power that holds steady matters more every day, especially where businesses run and grids serve homes.
- Fueled by rising factory output, power grid upgrades spark demand across the Asia Pacific. Electronics rules tighten as more gadgets hit homes and factories alike. This corner of the world moves quickest on the planet right now - driven harder by these shifts than anywhere else.
- Switching Voltage Regulators share approximately 63% in 2026. Last on the list but gaining fast, switching regulators climb as gadgets crave less waste in power use across machines and tech gear.
- Firm demand grows around three-phase regulators because the industry needs steady power, while big electrical systems rely on them too. Still, their role is not shrinking; instead, it expands where energy flow must stay balanced under load.
- Falling power needs push small-voltage controllers into phones, cars, and factory gadgets fast. Though tiny, their role grows where energy matters most.
- Fueled by rising demands for stable electricity, transmission and distribution networks now lead expansion efforts worldwide. Grid upgrades push these systems forward wherever energy needs grow more complex.
Not every component inside machines draws attention, yet voltage control quietly keeps operations stable. When incoming power fluctuates, regulators smooth the flow before delivering consistent output to sensitive equipment. Precision systems require uniform energy, as sudden spikes or drops can disrupt performance. As reliance on advanced electronics grows, regulated power has become more critical than ever supporting steady expansion of the voltage regulator market.
In environments filled with connected devices, stable voltage is essential. Homes and offices increasingly rely on smart technologies, each dependent on clean and uninterrupted power. Renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines introduce variability into power grids, creating fluctuating inputs that demand faster and smarter regulation. As sunlight shifts or wind speeds change, voltage swings must be managed efficiently. This dynamic energy landscape continues to drive innovation within the voltage regulator market.
Industrial facilities also depend heavily on voltage regulation to protect expensive machinery from damage caused by power surges. Consistent voltage extends the lifespan of heavy equipment, making regulators indispensable in manufacturing plants, automotive assembly lines, and data centers alike. Continuous advancements in circuit design have improved efficiency while reducing device size, enabling integration into compact and high-performance systems.
As industries evolve toward more automated, energy-efficient, and renewable-powered infrastructures, the voltage regulator market continues to grow—not due to trend-driven demand, but because stable power remains fundamental to modern operations. Without reliable voltage regulation, systems struggle to withstand fluctuating loads and uneven energy supply.
Voltage Regulator Market Segmentation
By Type
- Linear Voltage Regulators
Loud and clear operation marks these regulators when power needs stay small. Smooth delivery happens without extra sound getting in the way. A simple setup works well where energy demand does not climb high.
- Switching Voltage Regulators
Built to save energy, switching voltage regulators show up everywhere performance matters. Their design cuts waste, making them a go-to choice when power needs careful handling. Efficiency drives their popularity, especially where every watt counts. Found often in advanced electronics, they manage supply without slowing things down.
- Automatic Voltage Regulators
Stability begins here; voltage stays steady thanks to Automatic Voltage Regulators. These units work inside generators, holding levels firm even when supply shifts. Power moving through grids keeps a consistent flow because of their presence. When demand spikes or drops, they adjust without delay. Smooth performance across equipment follows naturally. Rare under their watch. Generators depend on them just as much as connected devices do.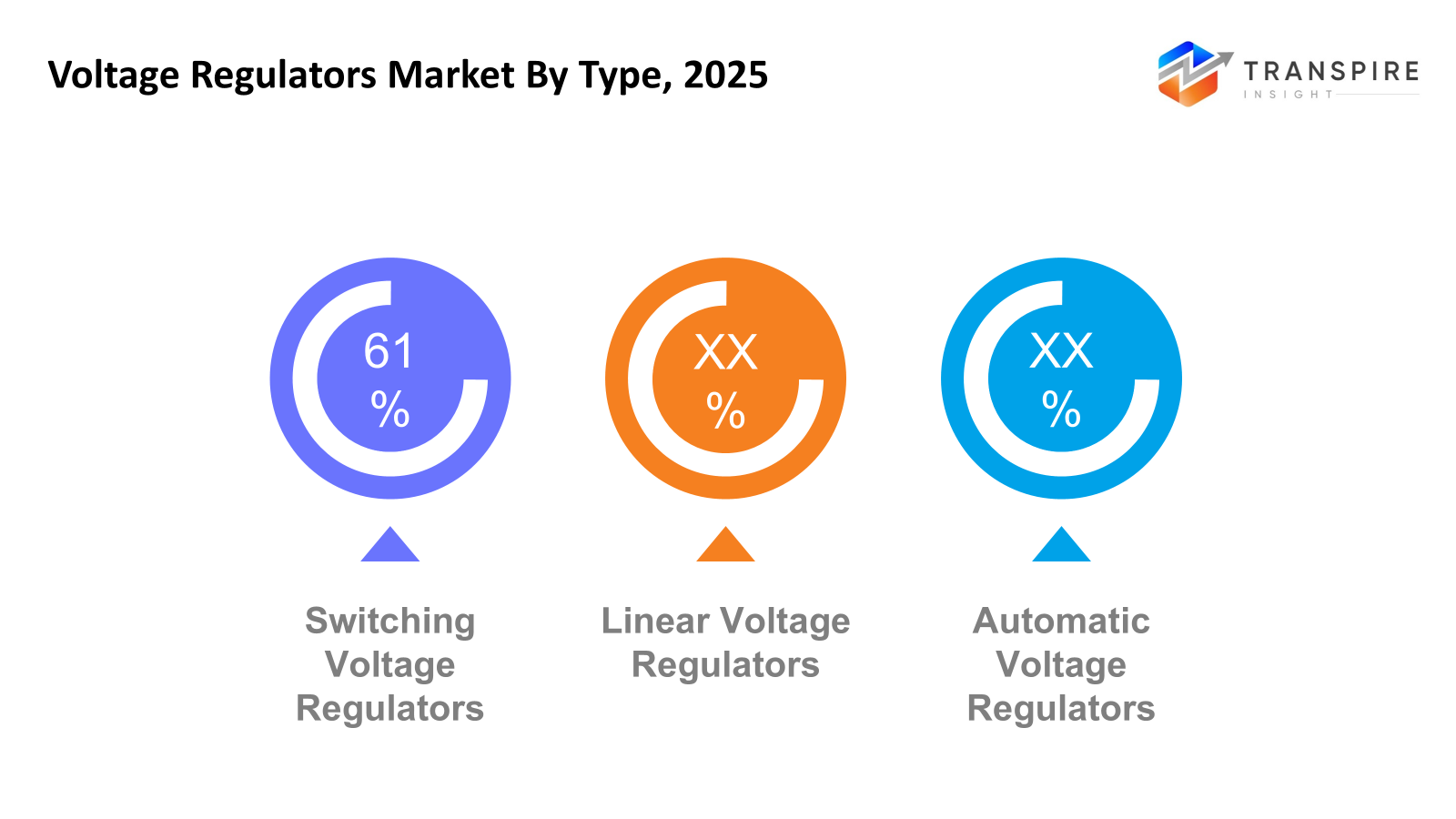
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Phase
- Single-Phase
One phase often powers homes plus smaller businesses. It’s typical that demand stays low.
- Three-Phase
Running on three separate currents, this system handles heavy-duty power needs in factories and big businesses. Heavy loads are managed thanks to its balanced energy flow across all phases. Built tough for places where regular setups just can’t keep up.
By Voltage Range
- Low Voltage
Folks plug these into gadgets and tiny machines when power needs stay low. A gentle stream of energy moves through household devices without strain. Small tools run on this quieter form of electricity every day. It keeps things humming at a safer, slower pace.
- Medium Voltage
Power in the middle range runs big machines at factories, plus lights and heat in large buildings. Equipment needing more juice than homes use often relies on this level of electricity. Not too high, not too low, just right for workplaces with heavy needs.
- High Voltage
Built for big power jobs, think long-distance lines, factories running hard gear. Power moves fast where demand runs high, skipping small steps. Heavy loads need a strong push, so voltage climbs to keep things flowing. Transmission paths rely on this force, pushing energy across stretches without slowing down.
By Application
- Power Generation
Keeping voltage steady in power stations comes down to how generators are managed. Voltage stays under control because systems respond when output shifts. When supply changes happen, adjustments keep everything balanced. Without these steps, fluctuations could disrupt delivery. Handling generation means watching small variations before they grow.
- Transmission & Distribution
Power lines move electricity while adjusting voltage for grid stability. Sometimes, higher pressure helps it travel far without losing strength. Equipment along the way keeps that balance steady. Transformers lower the intensity before reaching homes. Each section plays a role in smooth delivery.
- Automotive
Fuelled by motion, cars rely on a steady energy flow through their circuits. While electric models demand consistent voltage control across components.
- Industrial Equipment
Machinery stays safe from power spikes due to industrial gear. Voltage swings can not harm equipment when safeguards are in place.
- Consumer Electronics
A steady flow of power keeps gadgets running smoothly. Voltage stays flat, protecting delicate circuits inside machines. Equipment behaves better when the supply does not jump around. Sensitive parts last longer under stable conditions. Fluctuations fade into the background where they belong.
- Renewable Energy Systems
When sunlight fades or winds slow, renewable energy systems keep power steady. Because fluctuations happen, these setups balance what flows out. Even when nature changes pace, electricity remains smooth. Since generation varies, stability comes from smart adjustments. Though sources are unpredictable, delivery stays consistent.
Regional Insights
Out there in the Asia Pacific, more than anywhere else, voltage regulators see heavy use because factories keep running at full pace while people snap up gadgets nonstop. On top of that, governments push upgrades to electricity networks and smart grids, adding further pressure on reliable power flow. Think about China, India, Japan, then South Korea - each one cranking up factory robots and plugging in solar or wind farms faster than before. Because these shifts happen so fast, keeping voltage steady becomes less optional, more essential. Investment follows closely behind, pouring into new gear and local tech setups across the region. So it goes, the area stays ahead simply by moving quickest where others hesitate.
Most homes across North America already rely on modern voltage control gear. A long history of factory work, machines that run themselves, plus a real push to save power without failures. Out front stand the United States factories, which lean hard on smart regulators; cars use them more every year, even plants making electricity depend on precise voltage handling. Elsewhere, Canada updates its aging grids; down south, Mexico pushes solar and wind projects needing stable flow. Because everything connects so tightly now, new improvements spread fast - even small towns get access to newer fixes before they are outdated.
Different parts of Europe, Latin America, the Middle East plus Africa show uneven but promising expansion patterns. Driven by tough rules on energy use, Europe leans heavily into electric transport and intelligent electricity networks. Meanwhile, Latin American countries, along with nations across the African continent and the Middle East, see more funding pour into construction projects. A need for reliable electricity grows stronger in factories and businesses throughout these areas. Even if their overall size trails behind Asia Pacific and North America today, fresh chances appear as upgrades spread and electrical systems evolve.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- August 25, 2025 – Ferric launched a new voltage regulator for AI and High-Performance processors.
- June 18, 2025 – Hitachi Energy unveils compact line voltage regulator.
(Source:https://transformers-magazine.com/tm-news/hitachi-energy-unveils-compact-line-voltage-regulator/)
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 4.10 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 4.50 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 7.40 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 7.20% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, Eaton Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric, General Electric, Toshiba Corporation, Hitachi, Delta Electronics, Emerson Electric, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Infineon Technologies, ON Semiconductor, Vicor Corporation, ROHM Semiconductor, and Mean Well Enterprises |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Type (Linear Voltage Regulators, Switching Voltage Regulators, Automatic Voltage Regulators), By Phase (Single-Phase, Three-Phase), By Voltage Range (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage, High Voltage), By Application (Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution, Automotive, Industrial Equipment, Consumer Electronics, Renewable Energy Systems) |
Key Voltage Regulator Company Insights
A major name in the worldwide voltage regulator scene, Schneider Electric stands out through its wide range of power control and automated energy systems. Instead of just basic fixes, it delivers high-level voltage controls used in power grids, factories, server hubs, plus green energy setups. Across regions like North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, its footprint runs deep, driven by a sharp interest in intelligent grid tools and smarter energy use. By putting steady resources into digital electricity handling and eco-conscious frameworks, the firm keeps staying ahead without relying on flashy promises. Length stays true, details stay intact, just clearer now.
Key Voltage Regulator Companies:
- ABB
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens
- Eaton Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric
- General Electric
- Toshiba Corporation
- Hitachi
- Delta Electronics
- Emerson Electric
- Texas Instruments
- STMicroelectronics
- Infineon Technologies
- ON Semiconductor
- Vicor Corporation
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Mean Well Enterprises
Global Voltage Regulator Market Report Segmentation
By Type
- Linear Voltage Regulators
- Switching Voltage Regulators
- Automatic Voltage Regulators
By Phase
- Single-Phase
- Three-Phase
By Voltage Range
- Low Voltage
- Medium Voltage
- High Voltage
By Application
- Power Generation
- Transmission & Distribution
- Automotive, Industrial Equipment
- Consumer Electronics
- Renewable Energy Systems
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa











 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





