Market Summary
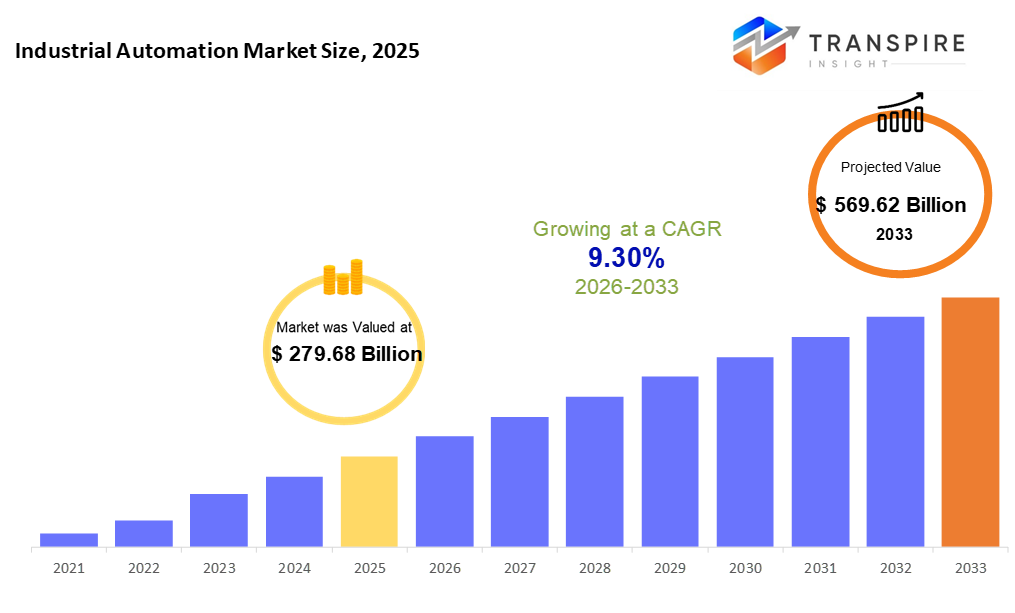
The global Industrial Automation market size was valued at USD 279.68 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 569.62 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.30% from 2026 to 2033. The industrial automation market is advancing due to increasing demand for enhanced production efficiency, precision, and safety across sectors like automotive, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Growth in robotics, machine vision, and industrial software is enabling smarter, flexible automation solutions. Rising adoption of programmable and flexible automation systems supports rapid product customization, while integration of sensory and controller technologies drives operational excellence and cost reduction globally.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 279.68 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 569.62 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 9.30%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- North America market share estimated to be approximately 36% in 2026. Fueled by modern factories, pricey workforces, and digital upgrades, North America leans heavily into smart machines. Though old-school production runs deep here, rising wages push firms toward robotic helpers. With Industry 4.0 reshaping norms, automated systems spread fast across plants. Where manual tasks once ruled, code now takes charge - quietly, steadily.
- In the United States, from coast to coast, factories shift fast -cars, gadgets, planes roll out quicker, smoother, tighter rules followed without delay.
- In the Asia Pacific, digital shopping surges through cities once slow to change. Machines learn faster where steel mills never sleep. Investors watch Tokyo, then move south. Growth hums in places remaking how things are built.
- The Controllers segment's expected market share will be 42% in 2026. Controllers like PLCs and DCS systems. These stay on top because companies want central oversight with instant feedback. Efficiency matters more when every second counts. Control shifts happen faster now, due to smarter automation setups.
- Scalable links to modern factory systems keep it ahead. Its strength lies in shifting smoothly between tasks. Being ready for digital upgrades makes a difference. This kind of setup grows without needing full reworks. Adaptability defines its edge over others.
- Factories on wheels see most robot helpers at work due to machines building cars, tight production rules, and a need for zero flaws. Not just speed but exact moves shape how parts come together, hold up under tests, and meet standards without guesswork. This sector leads because consistency matters more than ever when putting vehicles together.
Starting with machines that run themselves, the industrial automation market covers companies worldwide making tools to handle factory tasks without people doing every step. These setups often rely on devices called PLCs or DCS units alongside parts that detect changes like heat or motion to keep things moving smoothly. Instead of hands-on work, robotic arms move items around while electric drivers turn wheels and gears where needed. Software jumps in, too, using programs such as SCADA or MES so operators can see what's happening during production from a screen. Factories building cars, gadgets, medicine, or canned foods depend on these systems just as much as plants refining oil or shaping metal do. By linking hardware and digital controls together, one result stands out: fewer errors, safer conditions, better timing, all without constant oversight.
Factories want speed, accuracy, and always the same results, especially when making huge amounts. Car makers, gadget builders, places that pack food and drinks, they all jump in because they must run smoothly, keep quality tight, and meet strict rules. A problem. Another one. So firms turn to machines to stay sharp, cut labor costs, and keep up without slowing down.
Fueled by strong industrial bases, North America and Europe sit at the forefront of the market. Their grip on advanced tech deployment gives them an edge, especially where policies push smart manufacturing forward. Across the Atlantic, nations like the United States, Germany, and France have woven automation deeply into car and gadget production lines. At the same time, movement in goods handling, storage zones, and chemical operations shows a quiet rise in automated tools driven more by daily demands than big announcements.
Fueled by swift factory expansion, the Asia-Pacific zone races ahead, lifted by booming output hubs in China, India, and Japan. Growth surges not just from machines but also from smarter systems weaving through daily operations. Factories there now lean heavily on robots, networked sensors, and intelligent programs that guess breakdowns before they happen. These tools bring live data flow, link steps across lines, and smooth out hiccups fast. Progress does not stop; new tech keeps arriving, while businesses push harder for speed and fewer errors. Long-term momentum looks firm as industries evolve and digital minds take root.
Industrial Automation Market Segmentation
By Component Type
- Controllers
From the top down, these setups run things smoothly, PLCs or DCS handling tasks while keeping an eye on operations as they happen.
- Sensors and Transmitters
From heat to movement, sensors catch changes in machines. These tools track how much stuff is inside tanks. Pressure shifts get noticed right away by smart transmitters. Flow speed through pipes shows up clearly on monitors. Position checks happen constantly during operations.
- Robotics & Machine Vision Systems
Automation in factories comes from robots paired with visual sensing tools. These setups handle production jobs, check quality, and move goods without human effort along the way. Machines see what they do, react, and adjust all while running day after day.
- Industrial Software
Factories run on special computer tools. These handle tasks like monitoring machines or designing parts. Some track production steps across a plant. Others help workers interact with equipment using screens. Design programs let engineers build digital models before making real items. Data analysis tools find patterns to improve performance. Each type supports smoother daily operations.
- Drives and Motors
Motion control gets a boost from variable frequency drives, along with servos and steppers that move exactly when needed. Actuators join in, turning signals into physical shifts, smooth and accurate.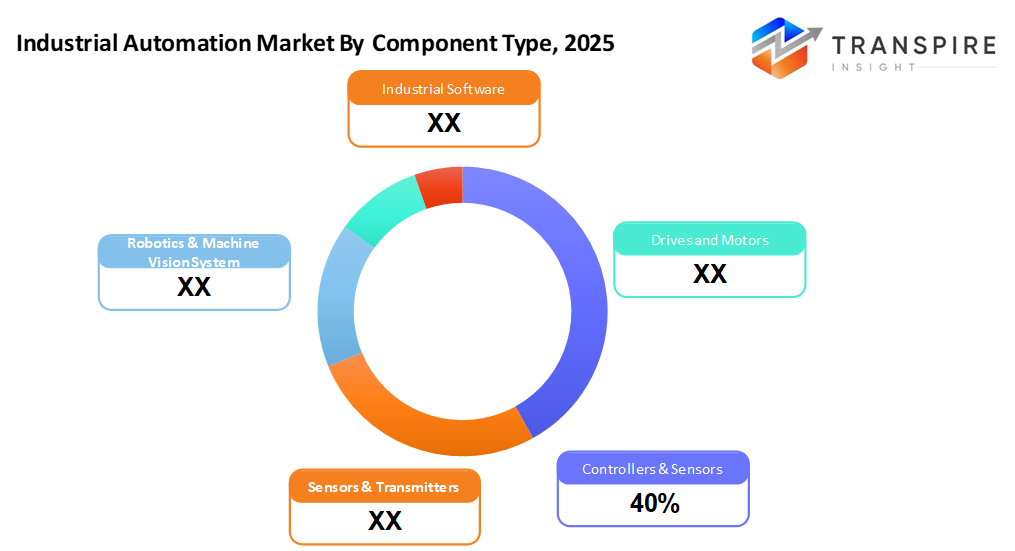
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Automation
- Fixed Automation
Few changes are possible once running fixed automation handles high output with steady repetition. Best suited when tasks stay the same over long stretches.
- Programmable Automation
When products change often, these systems adapt easily. Built for batches, they shift tasks without needing new hardware. Flexibility matters most when runs are short. What works today can switch tomorrow, no extra machines required.
- Flexible Automation
Systems that shift easily between making different things, needing almost no setup time. These setups adjust on the fly, handling variety without slowing down.
By End-Users
- Automotive
Robots help build cars, handling tasks like putting parts together automatically. One example is joining metal pieces through precise welding work. Painting gets done evenly without human touch. Making engines faster when machines take over steps. Each job runs more smoothly because robots repeat actions exactly.
- Electronics & Semiconductor
Robots place tiny parts on circuit boards, one step at a time. Machines build silicon chips under cleanroom conditions, layer after layer. Tests run nonstop on finished units, checking each signal path. Precision tools move without human hands, guided by sensors and code.
- Food & Beverages
Machines handle steps like filling bottles, sealing packages, sorting items, and then stamping labels in food and drink production.
- Pharmaceutical & Healthcare
Robots mix medicines now, one step at a time. Machines seal each pill into containers without help. Cameras check every batch for flaws right after. Mistakes have happened less since these tools arrived.
- Oil & Gas
Pipes hum under watchful sensors, guiding crude from earth to refinery. Machines track pressure while alarms stand ready. Out where rigs drill, systems respond fast to shifts underground. Equipment adjusts without waiting when leaks appear. Fields rely on steady signals to keep fuel moving. Safety switches act before danger grows too close.
- Others
Fabrics, synthetic materials, printed matter, metallic parts, each shaped by automated systems in factories far from tech's spotlight.
Regional Insights
Right now, factories in North America plus Europe run some of the smartest production lines due to long-established systems, deep tech use, and serious moves into digital factory upgrades. The United States, along with Canada sit at the top there, using high-end robots and control gear mostly in car plants, chip labs, and plane makers. They are just starting to bring in similar tools, especially near big factory zones that make vehicles. Over in Europe, powerhouses such as Germany, France, Italy, and the United Kingdom dominate not only because they build a lot but also due to helpful rules and a need for exact engineering work. Meanwhile, countries like Spain, Poland, and those up north are slowly weaving more automated setups into their daily runs, touching areas beyond just heavy industry.
Out of nowhere, Asia-Pacific leads global growth in industrial automation. Driven forward by fast-paced factory expansion and a surge in tech-powered plants, the area gains momentum. China, Japan, and India sit at the front, pulling demand higher. Big factories making cars, gadgets, or packaged foods now lean on robots more than before. Artificial intelligence guides machinery while internet-connected devices keep operations running. Meanwhile, nations like South Korea, Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam shift toward automated tools. Efficiency becomes a priority, labor expenses shrink, and output rises to match both local needs and overseas orders.
Down south, Brazil and Mexico lead the shift toward automated factories thanks to car makers, food producers, and heavy industry. Other nations nearby Argentina, Chile, and Colombia are slowly upgrading their plants too, bit by bit. Across the ocean, places like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and South Africa pour money into smart machines to strengthen output and back key sectors like energy, chemicals, and agriculture. Farther out in that same region, smaller economies have barely started using these tools, yet room exists for progress as roads, power, and factories grow stronger.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- December 3, 2025 – ABB India launched a new machinery drive for industrial automation.
- October 14, 2025 – OMRON launched the Bengaluru automation center to advance India’s smart manufacturing future.
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 279.68 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 305.69 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 569.62 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 9.30% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
ABB Ltd, Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation Inc., Schneider Electric, Honeywell International Inc., Emerson Electric Co., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Omron Corporation, Fanuc Corporation, Kuka AG, Molex, KEBA, Pennar Industries, Messung Industrial Automation, Delta Electronics, Frugalhacks, and others |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Component Type (Controllers, Sensory and Transmitters, Robotics &Machine Vision Systems, Industrial Software, Drives & Motors), By Automation Type (Fixed Automation, Programmable Automation, Flexible Automation), By End-Users (Automotive, Electronics and Semiconductors, Food & Beverages, Pharmaceutical & Healthcare, Oil & Gas, Others) |
Key Industrial Automation Company Insights
A global force in industrial tech, Siemens AG shapes how factories run. Its tools help machines work smarter across countries. Not just hardware, the company builds digital systems too. Efficiency gets a boost where its solutions go live.
A German-based tech giant, Siemens AG, ranks among the world's key players in industrial automation. From factory controls to intelligent networks, its Digital Industries arm offers tools like programmable logic controllers, simulation models, and adaptive software platforms. Operations in close to 190 nations support steady progress in cleaner, smarter manufacturing methods. Technology shifts led by artificial intelligence and digitized infrastructure keep the firm at the forefront -without chasing trends. Its long-term bets on sustainable industry practices shape how factories evolve worldwide. Complex challenges meet practical responses under a framework built for adaptability. Global reach matches local execution, maintaining influence across evolving market needs.
Key Industrial Automation Companies:
- ABB Ltd
- Siemens AG
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Omron Corporation
- Fanuc Corporation
- Kuka AG
- Molex
- KEBA
- Pennar Industries
- Messung Industrial Automation
- Delta Electronics
- Frugalhacks
- others
Global Industrial Automation Market Report Segmentation
By Component Type
- Controllers
- Sensory and Transmitters
- Robotics &Machine Vision Systems
- Industrial Software
- Drives & Motors
By Automation
- Fixed Automation
- Programmable Automation
- Flexible Automation
By End-Users
- Automotive
- Electronics and Semiconductors
- Food & Beverages
- Pharmaceutical & Healthcare
- Oil & Gas
- Others
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa












 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





