Market Summary
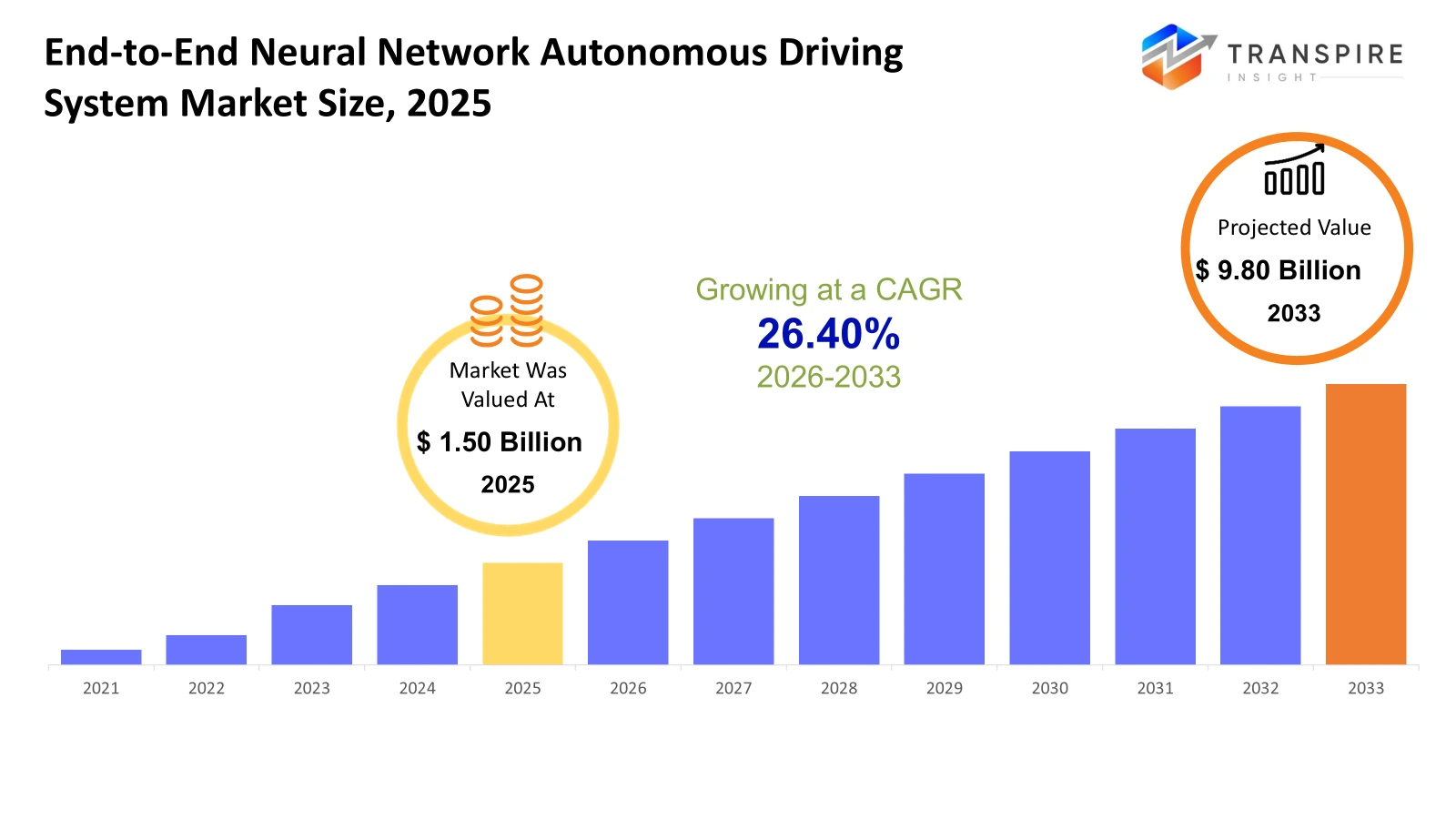
The global End-to-End Neural Network Autonomous Driving System market size was valued at USD 1.50 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9.80 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 26.40% from 2026 to 2033. Smarter software learns fast, computes quicker. Cars pack more self-thinking tech - safety climbs, mistakes fall, motion flows better. Progress in thinking circuits pushes car builders forward. They shift focus toward full auto control, aided by smart helpers inside vehicles. Speed of change surprises even experts watching closely.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 1.50 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 9.80 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 26.40%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- The North American market share is estimated to be approximately 80% in 2026. Ahead of most regions, North America thrives on strong research systems that feed new ideas into real-world tests. Pilot initiatives pop up where startups meet government backing, shaping how self-driving tech moves forward. Collaboration ties labs to industry players, turning experiments into market-ready tools without grand promises or shortcuts.
- Faster movement in the United States market comes as car builders link up with technology companies, pushing smart driving systems that learn like brains. These partnerships help speed up how fast self-driving tools improve using networks modeled on neurons.
- Fueled by major spending, Asia Pacific pushes ahead with fast smart transport systems now rolling out alongside self-driving trials. On top of that, artificial intelligence networks are expanding quickly to handle massive real-world use. Momentum here does not slow, driven by scale and steady tech integration across cities.
- Software shares approximately 57% in 2026. Faster progress now shows in programs that learn from patterns, since smarter math rules handle tricky road moments while pushing self-driving cars closer to full independence. Yet every step forward depends on how well machines adapt when traffic gets unpredictable.
- Fewer trucks than cars on roads lately. Cars move most people these days. Buses trail behind in numbers. Most trips happen in personal vehicles. Vans count too, but less often. That makes passenger models lead clearly
- Few cars on the roads today lack some form of driving aid, pushed forward by what people want. Features that help steer, brake, or stay in lane arrive first because buyers ask for them. Slow steps toward self-driving matter less than immediate usefulness. Choice shapes progress more than technology itself.
- Now showing up more often, Level 3 automation mixes self-driving ability with rules that allow it, so drivers can take their hands off the wheel under certain situations.
- Last on the list but biggest in size: Automotive OEMs take the lead. These makers of vehicles stand out when sorted by customer type. Though others exist, they claim most attention here
- Facing new tech shifts, carmakers push full-chain neural networks into upcoming models. Though complex, these systems shape how vehicles learn tasks over time. Some rely on layered data paths; others rebuild decision logic from the ground up. Driven by real-time demands, manufacturers weave smart circuits deep inside driving functions. Where older methods fade, fresh approaches take hold - silently, steadily. Each design step ties back to faster response needs across highways and cities alike.
One step ahead, car makers and tech firms are accelerating efforts toward fully autonomous vehicles, fueling rapid growth in the end-to-end neural network autonomous driving system market. Instead of relying on traditional rule-based and modular software stacks, advanced neural networks trained on vast volumes of real-world driving data now take control. These brain-inspired models transform camera, radar, and sensor inputs directly into driving actions without rigid, pre-coded instructions. Through deep layers of machine learning, they adapt dynamically when traffic conditions become complex. Guided by experience rather than fixed logic, these systems are redefining how vehicles interpret and respond to their surroundings.
Breakthroughs in AI, along with progress in sensors like lidar and cameras, keep pushing this field forward. With bigger budgets flowing into improving how cars see, anticipate, and react, systems now adjust faster to what happens around them. Momentum builds quietly as big carmakers and fresh startups alike turn toward smarter algorithms and flexible self-driving frameworks.
Rules around safety shape how the market moves, since officials aim to set guidelines for checking and using self-driving tech. Even though staying safe matters most, growing teamwork among companies and regulators opens smoother routes for trials and launch plans. People want cars that make life easier and feel safer, pushing makers to build smart full-system networks into future models.
Working alongside one another, tech companies, car makers, and software builders push for faster progress through joint efforts. Because shared goals matter, strong data networks, test simulations, and cloud platforms grow more central for teaching smart systems widely. Over time, what stands out is dependability, whether people feel confident using it, and how well it fits into everyday transport options; these shape lasting success.
End-to-End Neural Network Autonomous Driving System Market Segmentation
By Component
- Hardware
Sitting under the hood, sensors team up with AI chips to handle live traffic info. Cameras feed visuals while processors juggle decisions on the fly. Real-time reactions come alive through smart hardware links. Driving itself gets powered by these working parts behind the scenes.
- Software
Running beneath everything, software handles how systems see, think, and act using patterns learned from vast amounts of data. Instead of fixed rules, it adapts by recognizing similarities across examples. What emerges is a kind of judgment shaped by exposure, not programming. These networks mimic brain-like connections, adjusting strength based on experience. Decisions form gradually, layer after layer, without clear breaks. Behind each move lies a trail of weighted guesses refined over time.
- Services
System integration comes first, followed by thorough validation checks. Testing happens through realistic simulations, ensuring everything works as expected. Software stays current thanks to ongoing updates rolled out regularly. Each step connects directly to reliability, without extra layers or delays.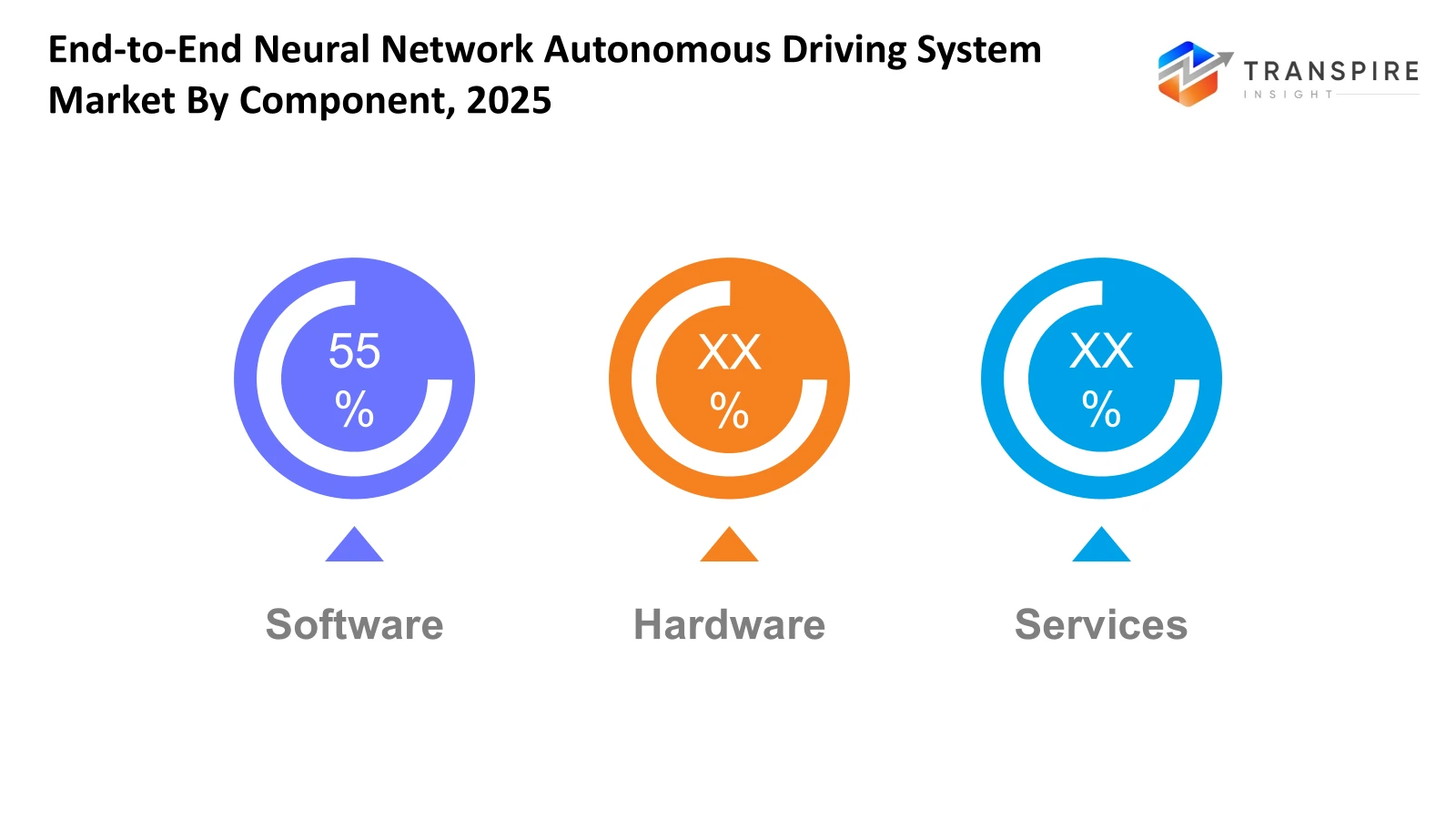
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Vehicles
Lots of people want cars that help them drive, so makers add more tech. Because of this need, passenger vehicles now come packed with tools to steer themselves a little. These days, most drivers expect some self-driving parts when they buy a new car. That shift pushes companies to include such systems in nearly every model out there.
- Commercial Vehicles
Built to move goods smarter while cutting risks on roads. Automation rolls in slowly, making each trip more reliable than before.
- Robotaxis
Emerging segment leveraging fully autonomous neural network systems for mobility-as-a-service.
By Level of Autonomy
- Level 2
Fully aware of surroundings, yet still relies on a person nearby just in case things shift fast. Still hands-on when needed, even if helping most of the way through.
- Level 3
When certain situations occur, the vehicle handles driving tasks on its own. Driving control shifts to the tech under preset circumstances. In particular environments, operation is taken over by the system automatically. Specific scenarios trigger self-managed motion through built-in responses. Under defined limits, movement unfolds without human input.
- Level 4
At Level 4, systems run almost entirely on their own within set conditions. Operation happens without constant oversight once boundaries are established. These setups handle most tasks independently, relying on built-in rules. Human presence is still needed, but only for rare cases. Performance stays consistent as long as the surroundings remain predictable. Intervention occurs solely when situations fall outside normal patterns.
- Level 5
At Level 5, vehicles handle every driving task without a person behind the wheel - ever. Conditions make no difference; control stays entirely with the system. Driving becomes something the machine does alone.
By End-Users
- Automotive OEMs
Fleet makers now weave full-range brain-style tech into upcoming models. Machines learn tasks from start to finish inside new rides. Smart circuits run through every stage of driving hardware. Vehicles gain built-in learning networks across future lines.
- Autonomous Vehicle Technology Companies
From deep learning codes up through sensor interpretation layers, firms building self-driving systems craft the brains behind driverless motion. Their tools let machines see surroundings, predict movements, and then decide actions without human input. Running on complex code frameworks, these platforms shape how vehicles navigate city streets and highways alike.
- Fleet Operators & Mobility Service Providers
Fleet operators find new paths using self-driving tech in transport networks. Mobility providers shift toward driverless options for city travel needs. Ride services run without human drivers, changing how people move around. Goods delivery adapts through automated fleets moving packages across regions. Shared rides evolve as machines take over steering tasks daily.
Regional Insights
Out here in the Asia Pacific, self-driving technology is gaining speed fast. Boosted by big spending from carmakers and tech leaders, progress thrives on artificial intelligence uptake across the area. Instead of waiting, nations such as China, Japan, and South Korea jump into wide-ranging test runs. Rules evolve quickly alongside factory strengths, helping brain-like software roll out in vehicles sooner. Urban transport upgrades blend with digital city plans, adding force behind driverless solutions taking root widely now.
Every so often, new progress shows up where engineering meets real-world testing. Heavy investment flows into projects that train machines to navigate as humans do. Companies across the United States build vehicles capable of learning from their surroundings using layered feedback loops. Behind the scenes, government initiatives keep pace with technological shifts through targeted financial backing. Labs turn ideas into functional systems thanks to well-established manufacturing channels. Progress unfolds steadily, rooted in live trials managed by major automakers and coders working side by side. Validation happens constantly, shaped by how algorithms adapt during actual road conditions.
Across the globe, Europe stands out by building on long-standing car manufacturing roots and tough safety rules to support smarter self-driving tech. In nations like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France, progress comes through shared science efforts and real-world test runs, because regulations slowly move together. Elsewhere, parts of Latin America, along with areas across the Middle East and Africa, are inching forward with funding-focused initiatives, launching small-scale trials as cooperation between governments and businesses grows. These moves respond to local transport needs while laying groundwork so automated travel might work better later.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- April 23, 2025 – ai launched AV software for up to SAE L4 autonomous driving.
(Source: https://www.therobotreport.com/helm-ai-launches-av-software-for-up-sae-l4-autonomous-driving/)
- May 05, 2024 – XPENG launched the industry’s first AI-enabled powered in-car OS, promoting an AI-enabled smart driving experience.
(Source: https://www.xpeng.com/news/018f968985698f616d3f2c9e8f720154)
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 1.50 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 1.90 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 9.80 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 26.40% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Tesla, Waymo, Cruise, NVIDIA, Mobileye, Baidu Apollo, Pony.ai, Aurora Innovation, Zoox, Argo AI, Motional, XPeng, Huawei, Toyota Research Institute, General Motors, Ford Motor Company, and Volkswagen AG |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Vehicle Type (Passenger Vehicles, Commercial Vehicles, Robotaxis), By Level of Autonomy (Level 2, Level 3, Level 4, Level 5), By End-Users (Automotive OEMs, Autonomous Vehicle Technology Companies, Fleet Operators & Mobility Service Providers) |
Key End-to-End Neural Network Autonomous Driving System Company Insights
Out front in the race for self-driving cars using full neural network systems, Tesla pushes ahead with its FSD system, rooted in deep learning from start to finish. Real miles driven by actual owners around the world feed raw experience into constant model upgrades. Instead of relying on outside parts, custom silicon made inside the company works hand in hand with proprietary code and wireless updates that evolve performance over time. This tight loop of hardware, brainpower, and live feedback keeps Tesla shaping what driverless tech can do next.
Key End-to-End Neural Network Autonomous Driving System Companies:
- Tesla
- Waymo
- Cruise
- NVIDIA
- Mobileye
- Baidu Apollo
- ai
- Aurora Innovation
- Zoox
- Argo AI
- Motional
- Xpeng
- Huawei
- Toyota Research Institute
- General Motors
- Ford Motor Company
- Volkswagen AG
Global End-to-End Neural Network Autonomous Driving System Market Report Segmentation
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Vehicles
- Commercial Vehicles
- Robotaxis
By Level of Autonomy
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
By End-Users
- Automotive OEMs
- Autonomous Vehicle Technology Companies
- Fleet Operators & Mobility Service Providers
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa













 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





