Market Summary
The global Carbide Tools market size was valued at USD 18.50 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 31.00 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.60% from 2026 to 2033. Growth in the worldwide carbide tools sector continues at a reliable pace, fueled by stronger needs from car makers, plane builders, and shops where metal accuracy and toughness matter most. Because factories now rely more on smart machines and computer-guided equipment, there's greater pull for cutting instruments that deliver under pressure.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 18.50 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 31.00 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 6.60%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market

To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- The North American market share is estimated to be approximately 30% in 2026. Flying high in the skies matters more here, where making complex machine shapes progresses across the region. Equipment built today helps power tomorrow’s designs without delay.
- From factories to workshops, the United States heavy industry keeps growing machines using computer control, helping spread tough cutting tools across production lines. A steady push into modern manufacturing fuels demand, where hard metal parts become essential players.
- Factories rise fast across the Asia-Pacific. Cars roll off assembly lines at a growing speed there. Metal jobs multiply throughout the region. Machines hum louder each year. Workshops stretch wider into new zones. Production climbs without pause. Tools evolve to meet needs. Demand builds from constant motion.
- Milling Tools share approximately 41% in 2026. From tiny gears to engine frames, milling tools see growing use where tight specs matter. Precision work in planes and cars drives their role forward. Where accuracy rules, these cutters shape metal with care. Not just speed but exactness pushes demand up. Making parts that fit perfectly means relying on advanced mills more each year.
- Tools last longer when they have a hard coating. These materials handle heat better during cutting. A thin layer on the surface reduces friction. This means less damage over time. Performance stays high even under heavy use. Shops choose them because replacements are needed less often.
- Automation's rise pushes the need for carbide tools that work with CNC machines. These tools keep up as machine types evolve. More precise tasks favor CNC systems. Tools must match their speed and accuracy. Demand grows where manual steps fade out.
- People who drive cars now see more vehicles being built every day. Machines shaping lighter parts are working harder because of it. This pushes up how much these tools get used across factories.
Heavy industry continues to rely on carbide tools because they last longer and deliver higher cutting accuracy than conventional alternatives. In sectors such as automotive manufacturing and aerospace production, even minor errors carry high costs, making precision essential. As machining speeds increase, manufacturers are upgrading tooling systems to keep pace with higher productivity demands. The rapid adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies is further driving demand for durable, high-performance components, strengthening growth in the carbide tools market.
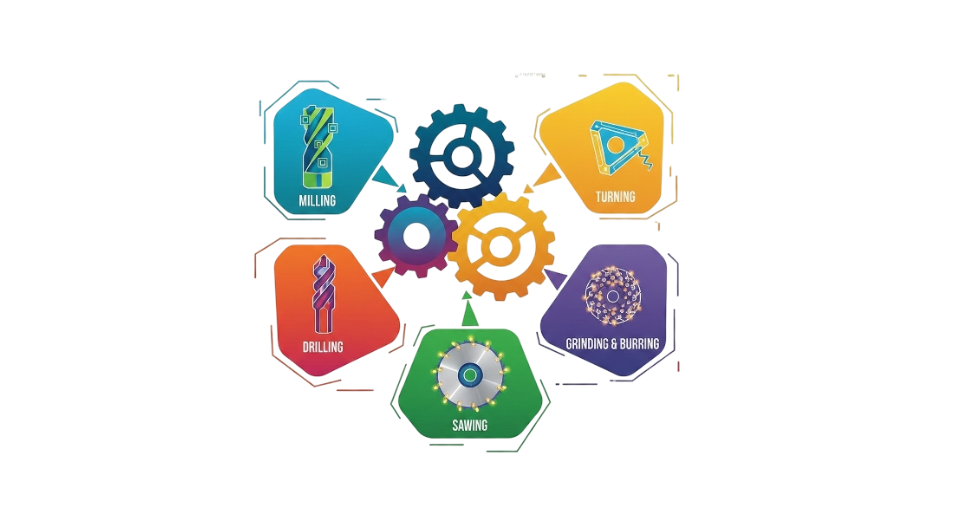
Metal shaping commonly depends on milling cutters, while drills are widely used for efficient hole-making operations. Turning tools play a critical role where tight tolerances are required during material removal. Saw blades support cutting across a range of materials, often operating in the background of production processes. Reamers refine existing holes to achieve smooth finishes, and taps form internal threads to meet precise assembly needs. Each tool serves a specific function based on application requirements, with milling cutters often preferred when complex contours and profiles are involved.
Over time, material quality has shifted how buyers act. Because of tougher performance needs, coated versions now see wider use where lasting power matters most. Even so, older uncoated kinds still hold ground when jobs stay routine. With better layers and shapes emerging, tools last further into tough tasks. Each small design jump adds up to smoother work overall.
With machines running faster now, tools must keep up without losing accuracy. Because automation grows, especially in CNC systems, tougher cutting tools become essential. In fields like car making or plane building, workers need better carbide cutters every day. Even factories producing small electronic parts rely on sharper, longer-lasting tools. New designs appear regularly, driven by real needs instead of trends. Progress happens quietly through constant tweaks rather than sudden leaps.
Carbide Tools Market Segmentation
By Tool Type
- Milling Tools
That job often falls to milling tools. These devices carve materials with accuracy. Instead of rough handling, they apply steady force. Precision matters most here. Alloys respond well to their consistent motion. Cutting happens gradually. Each pass removes a thin layer. Results show clean edges. The process repeats until complete.
- Turning Tools
Made to shave material precisely on lathes. Each cut is shaped by steady tool paths.
- Drilling Tools
A tool makes cuts through metal by spinning fast. Holes appear where force meets surface. Some versions handle tough stuff like steel or stone. Speed matters when pushing into solid layers.
- Sawing Tools
Blades that slice metal show up in factories where heavy-duty work happens. Cutting tough stuff means needing tools built to last, ones that handle pressure without bending.
- Other
Specialized cutters appear alongside them now and then.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Material Grade
- Uncoated Carbide
Hard metal without coating works well for everyday cutting jobs. These tools handle regular workshop tasks reliably. Built tough, they perform consistently across common materials. Their straightforward design supports dependable results. Most machinists keep them on hand for routine work.
- Coated Carbide
Hard coating on tungsten mix boosts life span while cutting better under pressure.
By Machine Type
- Uncoated Carbide
Fine-tuned gear that runs by code instead of hands. Computers steer every cut through programmed steps. These machines shape materials with tight accuracy again and again.
- Coated Carbide
Sometimes old-school gear works just fine with regular tools made for hands-on operation.
By End-Users
- Automotive
Under the hood, tools shape engines one piece at a time. Moving gears through production needs precise gear-cutting devices. Parts come together using machines built for tight fits.
- Aerospace
Flying machines need exact tools those used in making fighter jets rely on tight tolerances. Defense gear comes together through careful machining processes.
- Metalworking
Tools for general engineering and fabrication applications.
- Electronics & Electricals
Fine tools shape electronic parts with care during production. Machines work steadily when building electrical items. Crafted bits are cut exactly where needed in circuit work. Steady hands guide gear that forms tiny connections. Each piece fits true because of careful tooling.
- Other Industries
Construction sites use these tools too. Medical fields find them helpful now. Equipment in factories runs better because of this tech.
Regional Insights
Advanced tech in factories spreads fast across North America, thanks to big names in autos and aviation setting the pace. Precision work pushes the need for better machines, while moves toward automated systems add further pressure. The United States stands out within this zone because its industry backbone stays deep, with steady investment flowing into tool research. New methods in cutting gear often start here, fueled by constant testing and real-world trials. Growth does not hinge on one factor alone; it builds from layers of technical demand and practical upgrades over time.
Across Europe, strong demand comes from long-standing industries like car making, aircraft building, and metal shaping. Nations including Germany, Britain, and France push upgrades in factory tech, smart cutting systems, which boost the need for tough carbide cutters. Lately, more weight goes toward eco-friendly production methods, tools that last years, so coated, custom-grade carbides see wider use.
Fueled by surging factory output, vehicles rolling off assembly lines at a faster pace, alongside swelling demand in metal shaping and tech gear workshops, the Asia Pacific hums with change. Countries such as China, India, and Japan push ahead, powered by factories running nonstop, along with steady uptake of computer-guided cutting systems. Elsewhere, regions including the Middle East, Africa, and parts of South America inch forward, nudged by new roads, plants going up, plus shops upgrading how they make things. Machines that slice, drill, and shape using ultra-hard tips find more space on workbenches even there.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- January 28, 2026 – Carbide Snow Plow Blades and Cutting Edges Manufacturer SENTHAI Launches New Isolated Carbide-Edged Blade to Boost Road Safety and Lower Maintenance Costs
- March 31, 2025 – Seco launched a self-service platform to simplify carbide tool recycling.
(Source:https://www.etmm-online.com/seco-digital-platform-tool-recycling-a-7630ed44c4ae11c371047b3632473876/)
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 18.50 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 19.80 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 31.00 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 6.60% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Sandvik AB, Kennametal Inc., Walter AG, Kyocera Corporation, Sumitomo Electric Industries Ltd., Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, Iscar Ltd., Seco Tools AB, Guhring KG, Tungaloy Corporation, Ceratizit Group, Dormer Pramet, Ingersoll Cutting Tools, Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp., OSG Corporation, Allied Machine & Engineering Corp., and Mapal Dr. Kress KG |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Tool Type (Milling Tools, Turning Tools, Drilling Tools, Sawing Tools, Others), By Material Grade (Uncoated Carbide, Coated Carbide), By Machine Type (CNC Machines, Conventional Machines), By End-Users (Automotive, Aerospace, Metalworking, Electronics & Electrical, Other Industries), |
Key Carbide Tools Company Insights
Based in Sweden, Sandvik AB operates worldwide with a core focus on durable cutting instruments and specialized materials. From milling to drilling, their carbide solutions serve sectors like car manufacturing, aviation, and industrial machining. Instead of following trends, they pour resources into R&D, aiming to extend tool life and sharpen accuracy. Technology drives them forward, each advancement shaped by hands-on testing and real-world feedback. Across continents, factories rely on these systems because consistency matters more than speed. Leadership in this niche comes not from slogans but from decades refining what works. Performance under pressure defines their reputation - not promises, but results built one cut at a time.
Key Carbide Tools Companies:
- Sandvik AB
- Kennametal Inc.
- Walter AG
- Kyocera Corporation
- Sumitomo Electric Industries Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Materials Corporation
- Iscar Ltd.
- Seco Tools AB
- Guhring KG
- Tungaloy Corporation
- Ceratizit Group
- Dormer Pramet
- Ingersoll Cutting Tools
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp.
- OSG Corporation
- Allied Machine & Engineering Corp.
- Mapal Dr. Kress KG
Global Carbide Tools Market Report Segmentation
By Tool Type
- Milling Tools
- Turning Tools
- Drilling Tools
- Sawing Tools
- Others
By Material Grade
- Milling Tools
- Turning Tools
- Drilling Tools
- Sawing Tools
- Others
By Machine Type
- CNC Machines
- Conventional Machines
By End-Users
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Metalworking
- Electronics & Electrical
- Other Industries
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa












 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





