Market Summary
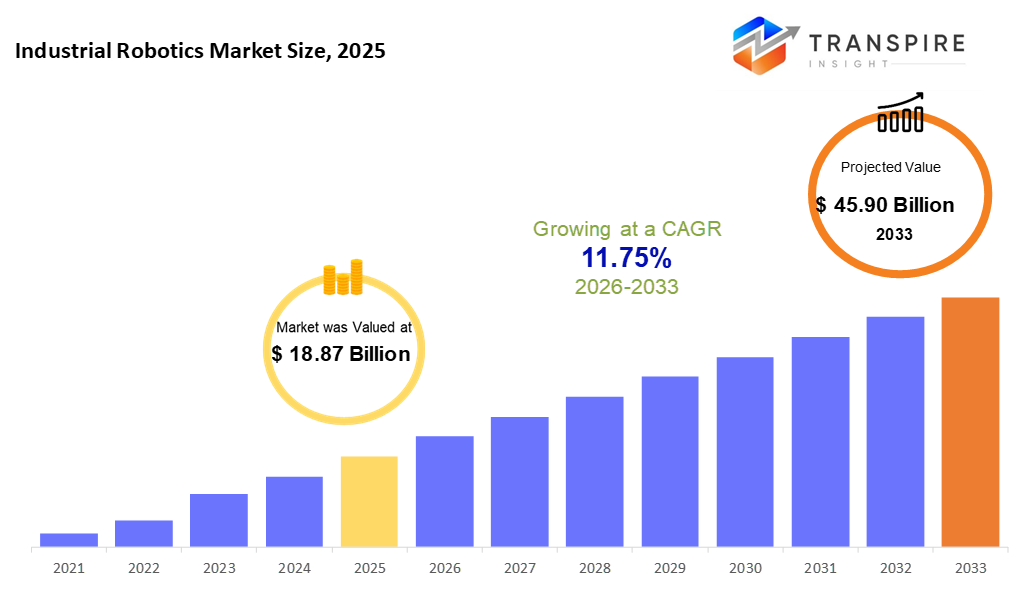
The global Industrial Robotics market size was valued at USD 18.87 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 45.90 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.75% from 2026 to 2033. The market is driven by rapid automation adoption across manufacturing industries to improve productivity, precision, and operational efficiency. Rising labor shortages, increasing demand for smart factories, and advancements in AI-enabled and collaborative robots are further accelerating industrial robotics deployment.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 18.87 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 45.90 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 11.75%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- North America market share estimated to be approximately 30% in 2026. Factories get smarter across North America, pushing growth through new production methods. Automation in car making plays a big role, too. Technology upgrades reshape how things are built, step by step.
- Backed by state backing, factories are updating fast, and machines that learn found steady growth across the United States. New tech adoption rose where policy met progress. Automation moved ahead thanks to shifting industry needs paired with smarter tools working alongside people.
- China, Japan, and South Korea push ahead with industrial growth surges here. Machines take on more tasks across factories every year. Momentum builds fast thanks to rising production rates. This part of the world moves quickest now, fueled by new tech in everyday work.
- Articulated Robots share approximately 44% in 2026. Few robots match articulated ones when it comes to tricky jobs. These machines bend and reach where others cannot. Flexibility gives them an edge in welding work. Tasks like putting parts together come naturally to them. They handle that too. Their design allows smooth motion across many angles. That is why they still lead the pack.
- Payloads between 5 and 50 kilograms. These handle mid-level tasks well. Found often in auto manufacturing. Also common when moving everyday products. Performance fits demand perfectly.
- Material handling takes the lead. Automation pushes growth across shipping centers, packing stations, and storage spaces. Faster movement drives demand here.
- Fueled by automation needs, vehicles roll out faster thanks to robotic arms fitting parts together. Welding sparks fly as machines seal frames with steady hands. Paint jobs get smoother when bots handle spraying. Precision tasks once done slowly by people now move at machine speed.
Robots built for factory work now show up more often where products get made. Machines that bend, reach, turn fast, move straight lines, or team up safely with people handle jobs like putting parts together, joining metal, moving boxes, coating surfaces, and checking quality. Smarter software, cameras that see, and internet-linked systems help these machines do better, last longer, and adapt quicker inside today's high-tech production sites.
Fueled by climbing wages and tougher manufacturing demands, one big push comes from the hunt for sharper accuracy and smoother workflows. Leading the pack, vehicles still take top spot when it comes to robot buyers. Close behind, gadgets, heavy tools, processed meals, medicines now lean on machines more each day, fitting parts together, sealing boxes, checking standards. A quiet shift? Friendly bots that work alongside people, sneaking into smaller factories where space and budgets are tight.
A stronger focus on smart factories and digital upgrades ties robotics to artificial intelligence, data tools, and online networks to get more done. Another piece: rising needs in online shopping, shipping, and storage drive robot use for moving goods and placing items precisely. Support from public policies aimed at updating production lines also plays a role in widening the market.
Still, getting into this space takes serious money, tangled setup work, and demands trained people who know how to run robotic setups day after day. Even with those hurdles, fresh chances are popping up across growing areas, smaller factories, and even narrow fields like hospital labs where machines help handle tasks more smoothly. New types of robots, lighter, bendable, and able to team up safely with humans, are reshaping what is possible while cutting costs along the way.
Industrial Robotics Market Segmentation
By Type of Robots
- Articulated Robots
Flexibility from multiple joints makes articulated robots common in tasks like welding, where movement matters. Handling materials often relies on these machines when precision counts.
SCARA Robots
When it comes to placing small parts with care, SCARA robots often handle the task in car and gadget factories. These machines move quickly yet stay accurate during repeated steps. Some rely on them heavily, where tiny errors can cause big issues later down the line.
Delta Robots
Flying through tasks fast, these robots grab tiny parts without slowing down. Packaging jobs? They zip through those, too. Sorting bits by size or shape keeps them busy most days. Quick arms move like a blur when picking things up.
- Linear Robots
A straight-line mover takes on jobs like carving parts with precision tools, building objects layer by layer in printers, or shifting materials around a workspace. One common type follows grid-like paths to get tasks done efficiently across flat planes.
- Collaborative Robots
Robots that team up with people are built for tasks like putting things together, wrapping products, or checking quality. These machines fit right into shared workspaces without barriers. Safety comes first, so they slow down or stop when someone gets close. Tasks once done only by humans now get help from these helpers. Smooth moves, smart sensors, constant attention to where workers are. Not replacements, just partners in daily routines.
- Others
Built for unusual jobs, these handle round shapes or tube-like forms. Some tackle odd assignments, others can not manage. Unique builds fit tight spots where regular machines will not work.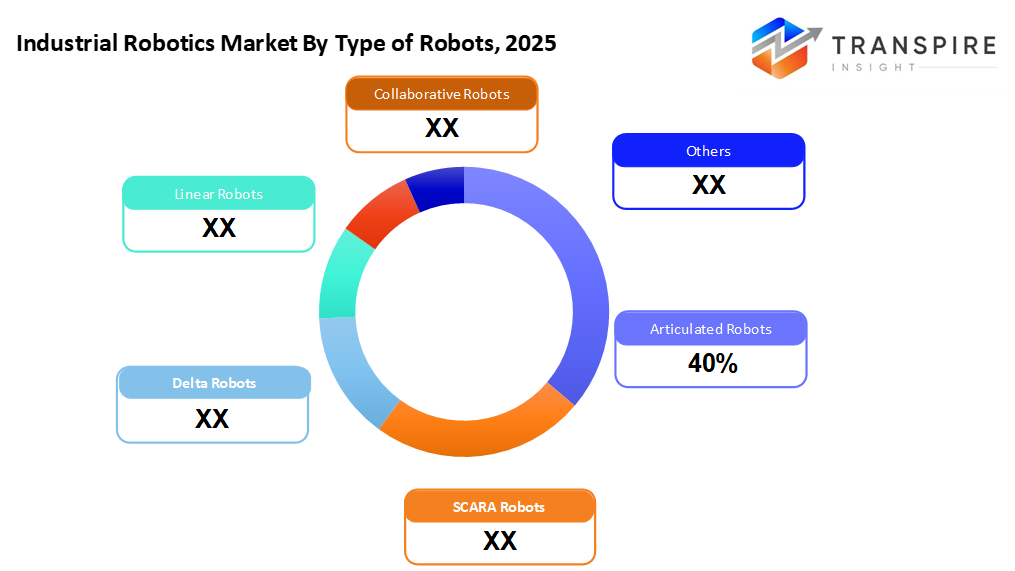
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Payload Capacity
- 0-5 Kg
Robots that handle up to five kilograms work well in making gadgets or tiny parts. These compact machines fit neatly into tight workflows where fine control matters most. Light-duty arms move components without taking up much space. Precision beats power here, especially when assembling circuit boards or health tools.
- 5-50 Kg
A single robot handles loads between 5 and 50 kilograms. These models move parts in car factories. Some fill tasks around household product lines. Others support routine factory work across industries.
- 50-500 Kg
A single heavy robot might lift half a ton. These machines work where big parts move - factories shaping steel, building vehicles, shifting bulky loads. Some handle as little as fifty kilos. Their strength fits tough industrial jobs needing power and precision.
- Above 500 Kg
- Robots weighing more than half a ton handle big jobs, space industry work, massive equipment assembly, or intense factory duties. These machines tackle what smaller units simply can’t manage due to scale. Built strong, they move huge parts with steady precision. Power and size define their role in complex industrial settings.
By Application
- Material Handling
Robots step in where tasks get repetitive, such as stacking boxes, wrapping items, and grabbing goods off shelves. Movement through warehouses changes when machines take charge of sorting and moving things around. Automation shifts how stuff flows from one spot to another, quietly reshaping daily operations behind the scenes.
- Welding
Fires spark when metal meets heat, common in car factories where pieces lock together under pressure. Machines hum during quick bursts that bind steel at exact points. Bright flashes light up workshops where strong frames take shape through steady arcs.
- Assembly
Built for tight tolerances, these machines fit parts together in phones, cars, and toys. One by one, they move, guided by sensors that never blink. Where humans tire, they keep pace without pause. Each motion calculated, every turn exact. Production hums when they run steadily through the night.
- Painting & Coating
A single brush stroke sets the scene. Machines now handle paint with steady precision. Across car factories and household item lines, robotic limbs spread layers without a hitch. One after another, surfaces come out smooth, thanks to motion programmed down to the millimeter. Not guesswork, just consistency, day in, day out.
- Pick & Place
Robots move fast when placing items into packages. These machines handle electronics without slowing down. Food production lines rely on their speed, too.
- Inspection & Quality Control
A single robot watches each piece move by, checking for flaws it was taught to spot. One camera measures width while another notes depth; differences too small for the eyes show up clearly. Mistakes get flagged before anything goes further down the line.
- Others
Robots handle tasks like filling containers, running labs, building parts layer by layer, and also work in unique factory settings.
By End-Users
- Automotive
Fueled by demand, cars lead in robot use tasks like joining parts, moving materials, coating surfaces, which show up often here. Machines stick around because precision matters most where speed meets scale.
- Electronics & Electricals
Robots move circuit boards through production lines. One machine places tiny parts with exact positioning. Testing units check each piece after placement. Machines work steadily during inspection phases. Automation handles delicate tasks without pauses.
- Metal & Machinery
Fires join steel beams when factories shape large parts. Heavy tools move metal, while machines cut paths through thick plates.
- Food & Beverages
Packaging tasks are handled by machines that move quickly between stations. Moving items into place happens without human hands touching them. Machines take over once raw ingredients enter the system.
- Pharmaceutical & Healthcare
Robots handle lab tasks, moving samples or running tests without help. Machines pack medicines into bottles or blister packs with precision. Cleanroom systems keep drugs safe from germs during production.
- Plastics and Chemicals
Filling molds, moving materials, wrapping products, and machines help shape plastic goods. Making containers, forming parts, and sealing packs takes steady robotic arms.
- Others
Flying machines, moving stuff around, everyday products, and niche production fields.
Regional Insights
Across North America, factories hum with robotic arms, especially in the United States, where heavy industry leans on machines more each year. Not just cars but circuit boards too, automation spreads through production lines like morning light. Because digital upgrades reshape how plants operate, robots fit right into new ways of working. When wages climb, companies often turn to mechanical helpers instead of hiring more people. Support from policymakers gives that shift an extra push forward. Innovation does not stop; it rolls ahead, guided by engineers testing smarter systems every season. This part of the world now runs on precision tech built slowly over decades.
Over in Europe, factories are turning more to robots, especially in Germany, France, and Italy. What stands out is precision work, along with smarter machines that learn and cooperate alongside people. Cars roll off automated lines while circuits get assembled by robotic arms. Rules here actually help innovation instead of slowing it down. Factories already well built for heavy industry now add digital brains. Money flows into labs where next-gen robots take shape. Electronics makers benefit just as much as those shaping steel. Growth hums quietly beneath the surface.
Out here in the Asia Pacific, things move fast because factories keep expanding, especially in China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Robots are rolling out faster than ever. Not far behind, Latin America inches forward as car makers and food producers bring in new machinery. Over in the Middle East and Africa, big projects in shipping, energy, and heavy industry begin leaning on automated systems more each year. A growing need for machines that save money yet adapt easily to different tasks. Speed, scale, and smart adjustments shape how robots spread across these lands.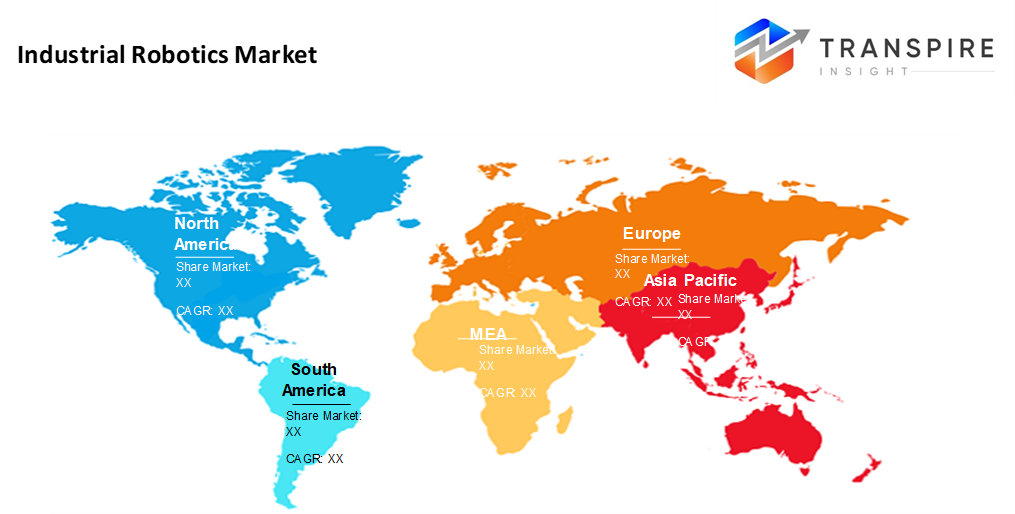
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- October 8, 2025 – SoftBank Group acquired ABB’s Industrial Robotics business for USD 5.40B, accelerating push into AI-driven automation.
(Source: https://techfundingnews.com/softbank-to-acquire-abbs-industrial-robotic-arm-for-5-4b-in-2026/
- June 26. 2025 – Apptronik launched Elevate Robotics to enter industrial automation.
- June 24, 2025 – ABB expands its large industrial robots portfolio.
(Source: https://new.abb.com/news/detail/127079/prsrl-abb-expands-large-industrial-robot-portfolio
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 18.87 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 21.09 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 45.90 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 11.75% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Fanuc Corporation, Kuka Global, ABB Ltd, Yaskawa Global, Mitsubishi Electric, Universal Robots, Epson, Staubli, Omron Industrial Automation, Kawasaki Robots, Comau, Denso Robotics, TM Robotics, Goeke Group, and Svaya Robotics |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Type of Robots (Articulated Robots, SCARA Robots, Delta Robots, Linear Robots, Collaborative Robots, Others), By Payload Capacity(0-5 Kg, 5-50 Kg, 50-500 Kg, Above 500 Kg), By Application (Material Handling, Welding, Assembly, Painting & Coating, Pick & Place, Inspection & Quality Control, Others), By End-Users (Automotive, Electronics & Electricals, Metal & Machinery, Food & Beverages, Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare, Plastics & Chemicals, Others) |
Key Industrial Robotics Company Insights
Fanuc lives in Japan but works everywhere. This firm builds machines that move like arms, twist like wrists, or work right beside people. Car makers, gadget factories, and metal shops all use these robots. Tasks include joining parts, moving things around, putting pieces together, and carving materials with care. Performance stays strong over time, which customers notice. Help comes fast, no matter the country. Smarter software now lets robots learn on their own. Internet links allow constant updates while running jobs. Factories get more aware, almost thinking for themselves. New ideas keep flowing here, shaping how machines are used across continents.
Key Industrial Robotics Companies:
- Fanuc Corporation
- Kuka Global
- ABB Ltd
- Yaskawa Global
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Universal Robots
- Epson
- Staubli
- Omron Industrial Automation
- Kawasaki Robots
- Comau
- Denso Robotics
- TM Robotics
- Goeke Group,
- Svaya Robotics
Global Industrial Robotics Market Report Segmentation
By Type of Robots
- Articulated Robots
- SCARA Robots
- Delta Robots
- Linear Robots
- Collaborative Robots
- Others
By Payload Capacity
- 0-5 Kg
- 5-50 Kg
- 50-500 Kg
- Above 500 Kg
By Application
- Material Handling
- Welding
- Assembly
- Painting & Coating
- Pick & Place
- Inspection & Quality Control
- Others
By End-Users
- Automotive
- Electronics & Electricals
- Metal & Machinery
- Food & Beverages
- Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
- Plastics & Chemicals
- Others
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa











 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





