Market Summary
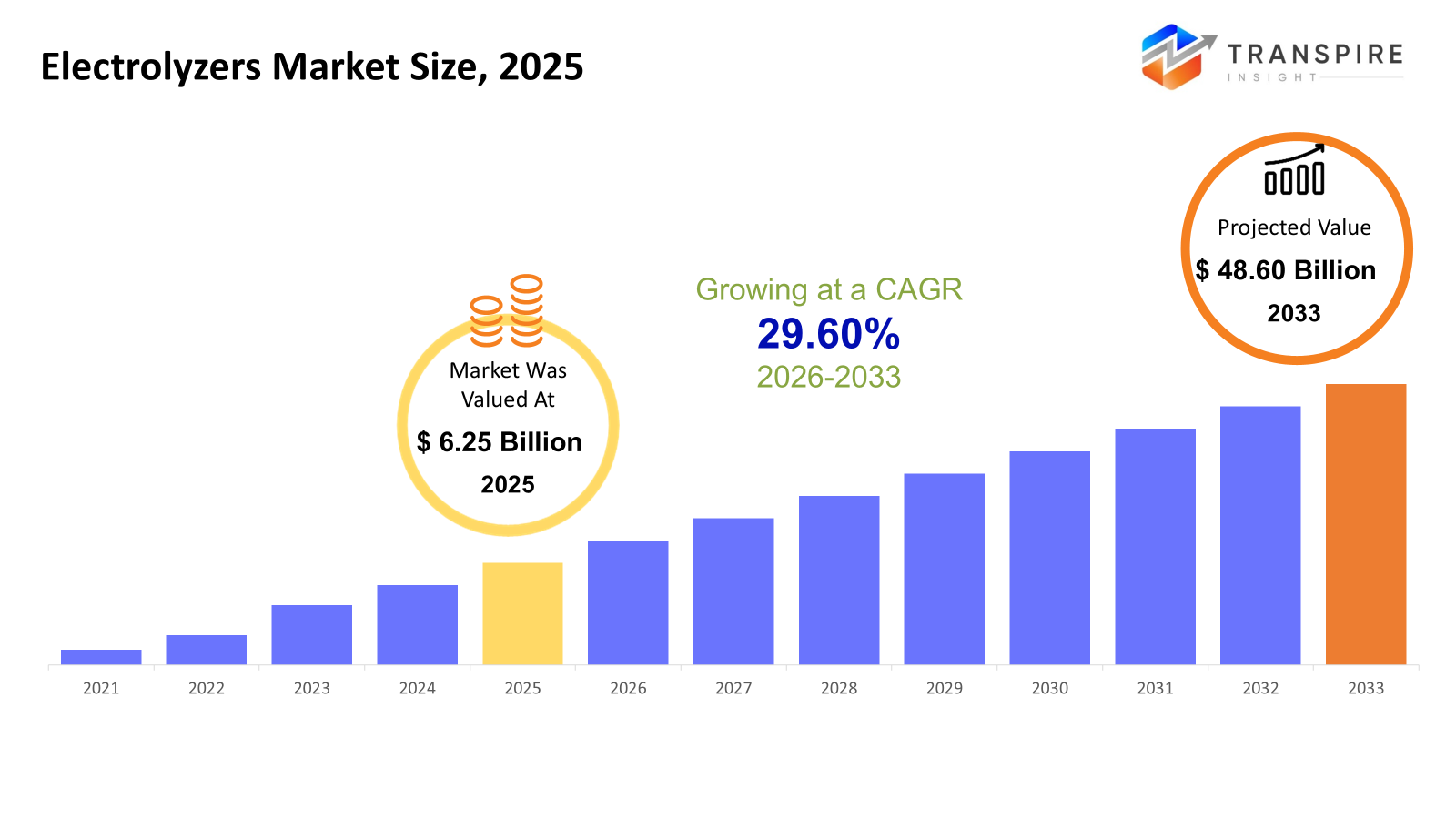
The global Electrolyzers market size was valued at USD 6.25 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 48.60 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 29.60% from 2026 to 2033.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 6.25 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 48.60 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 29.60%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- North America market share estimated to be approximately 30% in 2026. North America, fueled by government programs for clean hydrogen, expansion happens fast. Renewable energy efforts play a role, too. Power companies add electrolyzers, pushing the movement forward.
- United States fueled by public investment, progress gains speed. Hubs for hydrogen rise as a result of targeted support. Companies move ahead, guided by pledges to adopt cleaner alternatives.
- Asia Pacific surging demand across Asia stems from major investments by China, Japan, and South Korea into electrolyzers tied to both industry and green energy initiatives. These efforts aim squarely at cutting carbon emissions. Progress is most visible where factories link up directly with renewable-powered hydrogen systems.
- Proton Exchange Membrane shares approximately 55% in 2026. Fuel made by membranes is rising in efficiency gives it an edge. Speed matters when power shifts, so does fitting into wind or solar flow. Quick response keeps it ahead. Renewables pair well because nothing sits idle.
- Fresh momentum builds around 1–10 MW setups, fitting neatly into business and factory needs. Scale meets adaptability without tipping too far either way.
- Sure thing rolls through most setups, steady power keeps things running smoothly at big sites while helping save on expenses over time.
- Power needs grow, so hydrogen steps in to help store electricity, especially when sunshine or wind provides it. Sometimes, grids use it to balance supply from green sources. It fits where batteries fall short, moving energy across time. Fuel shifts follow, pushed by cleaner options gaining ground.
Right now, the push for cleaner power sources gives electrolyzers more attention than before. Water breaks apart into hydrogen and oxygen when an electric current passes through - this job belongs to electrolyzers. Their role matters because they help cut down harmful gases released by factories, power plants, and vehicles. As companies rethink how they use energy, these devices show up more often in heavy industry, public infrastructure, and even shipping routes.
Right now, different kinds of electrolyzers shape the field. Proton Exchange Membrane, Alkaline, Solid Oxide, and Anion Exchange Membrane stand out. Because they work efficiently and react quickly, PEM units fit well with wind or solar power setups. Even though newer options appear, alkaline types still hold ground thanks to lower costs and steady performance at big facilities. On the edges, SOE and AEM models begin finding roles where efficiency matters more or when setups need flexibility.
Fuel cells split water into hydrogen through machines that work in factories, power plants, or alongside wind and solar setups. These devices help store extra electricity when the supply runs high. Industries use the gas to make chemicals, move heavy vehicles, or replace fossil inputs in refining. Power providers watch demand shifts closely, turning surplus electrons into storable fuel. Oil firms test new methods to cut emissions without halting output. Trucks roll farther between refills thanks to compressed gas tanks under chassis frames. Factories once reliant on coal now blend clean molecules into heat systems.
Still gaining speed, the push for hydrogen keeps growing due to fresh backing from both public budgets and new rules. Across nations, officials are shaping policies, handing out funds, not just offering tax perks but building systems that favor clean fuel networks. Firms respond by pouring resources into testing ideas, refining tech, and rolling out massive production units. With steady momentum, electrolyzer technology finds itself central to shifting how power flows across continents. This shift opens energy paths that bend without breaking, last longer, and pollute less.
Electrolyzers Market Segmentation
By Type
- Alkaline Electrolyzers
These electrolyzers work well at making hydrogen on a large scale. They have been around long enough to prove reliable in factories. Cost stays low because the design is straightforward. Many industries choose them due to steady performance over time.
- Proton Exchange Membrane
When sunlight flickers or wind drops, these units adjust quickly. Their small size fits neatly into tight spaces. Because they link well with solar panels and turbines, power never sits idle. Built to react in seconds, not minutes.
- Solid Oxide Electrolyzers
Heat-powered electrolyzers work best when hot. These solid oxide types turn water into hydrogen more efficiently because of the temperature. Big setups could make lots of fuel without wasting energy. Their performance rises where heat is already available.
- Anion Exchange Membrane
Slower ions move through special membranes when electricity splits water. These setups borrow smart parts from two older types but cost less to build. Fewer rare metals are needed compared to high-end models. Some pieces still wear out faster than desired. Not yet common, though labs keep testing improvements.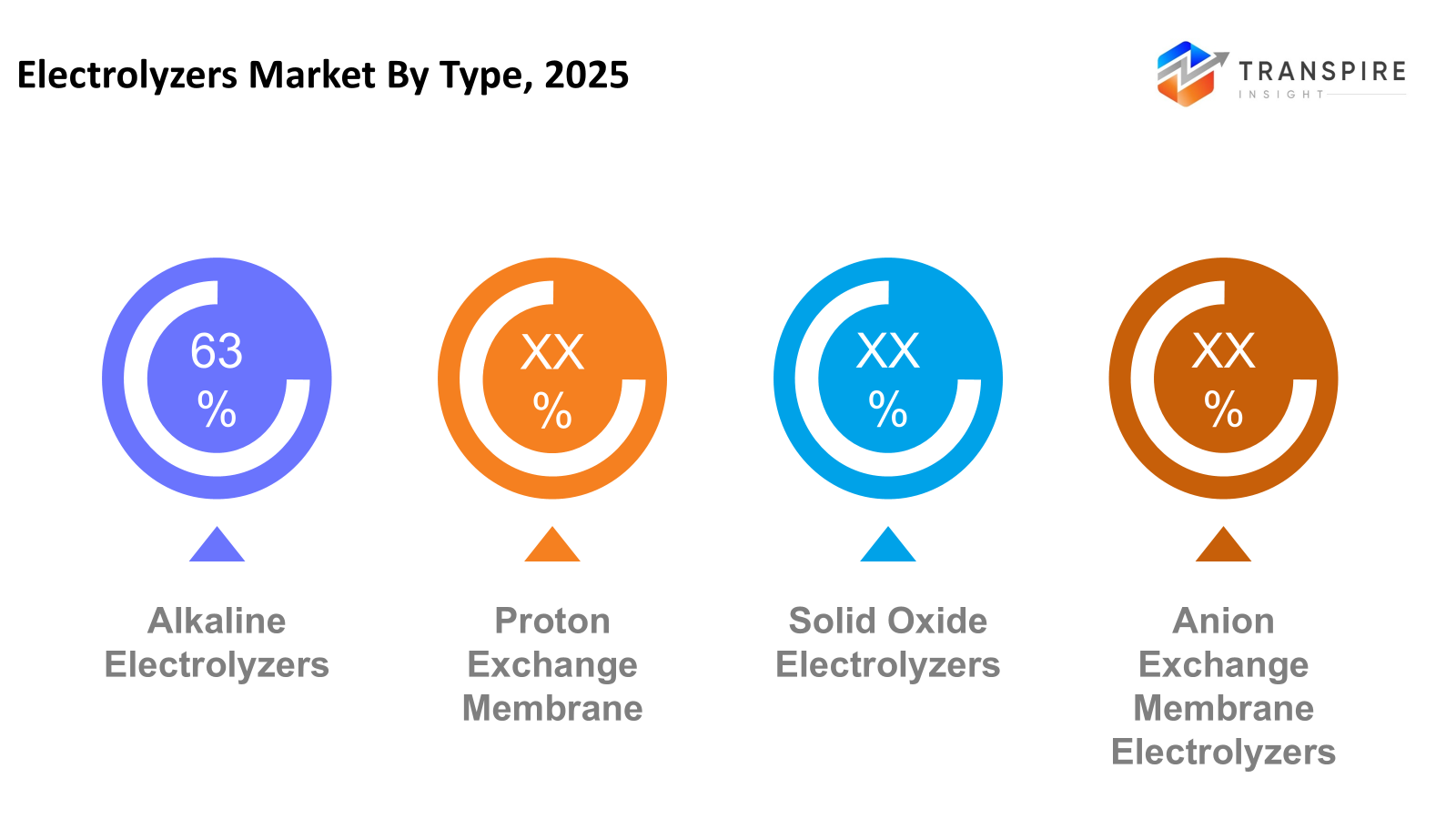
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Capacity
- 1–10 MW
Medium-scale solutions for industrial sites or localized energy systems.
- 10–100 MW
Large-scale plants for grid-connected or industrial hydrogen production.
- 10-100 MW
A hundred megawatts or more powers large installations tied to hydrogen centers, linking cleanly over the years ahead. These projects shape major energy shifts, often backing wide networks instead of small needs. Size here means lasting connections between green sources and future fuel systems.
By Operation Type
- Grid Connected
Hooked into the electricity network, these electrolyzers draw steady power while helping smooth out demand swings across the system.
- Off-Grid
Power that runs on its own, away from big grids. Usually found where cables don’t reach. Uses sun, wind, or water instead of fossil fuels. Works quietly in distant spots. Built to handle needs without outside help. Often seen in cabins, boats, or rural areas. Keeps lights on when nothing else can.
By End-Users
- Energy & Utilities
Power systems now tap hydrogen made on-site to store electricity, run turbines, plus balance wind and solar supply across grids.
- Oil & Gas
Fuel processing relies on it during refinement. Meanwhile, cutting carbon in fuels also depends on its role.
- Chemical & Petrochemical
Fuel for making ammonia kicks off the chain. Moving on, hydrogen steps into methanol creation. Other chemical paths rely on it too. Starting points shift, yet the role stays central.
- Industrial Manufacturing
Fuel made in factories helps shape steel, build tiny circuits, runs machines elsewhere too. Hydrogen flows where heavy work happens, tying into making things people use every day.
- Transportation
Fuel for hydrogen-powered vehicles and mobility solutions.
Regional Insights
North of the border, demand for electrolyzers climbs fast. Policies here push progress forward. Washington throws its weight behind the shift, backing hubs where hydrogen takes shape under public funds. Power companies join in too, linking machines that split water to wind and solar arrays spreading across open land. Farther north, rivers running deep supply steady electricity, helping factories store power using these same tools. Growth hums quietly, piece by piece, shaped by geography as much as goals.
Across Europe, nations push ahead with plans to install electrolyzers, aiming at cleaner energy and stronger supply chains. Germany takes charge alongside France and the Netherlands, where joint efforts between government and industry spark progress. Big wind and solar ventures link into hydrogen systems, shaping a new power landscape. Support comes from EU-wide rules and cash flows that speed up real-world use of older and newer electrolysis methods. Projects stretching across borders gain footing thanks to coordinated backing and shared goals.
Energy needs keep climbing across the Asia Pacific, pushing faster development in the sector. Government efforts to back cleaner options add momentum, while renewables grow stronger by the year. China, Japan, and South Korea take charge here, building systems that link hydrogen output to wind and solar supplies. Factories in these places now rely more on hydrogen made through green methods. In Southeast Asia, countries start turning to machines called electrolyzers not just for factories but also to store and manage electricity. Their expanding networks of renewable power help make this kind of hydrogen feasible. Progress moves step by step, powered by sun, wind, and water.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- December 9, 2025 – 10MW electrolyzers launched by Stargate Hydrogen.
(Source:https://stargatehydrogen.com/news/10mw-electrolyser-launch-aurora/
- March 27, 2025 – Enapter presents the world’s first AI-powered electrolyzers
(Source:https://enapter.com/en/press-release/enapter-presents-the-worlds-first-ai-powered-electrolyzer/
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 6.25 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 8.00 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 48.60 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 29.60% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Nel ASA, ITM Power, Plug Power, McPhy Energy, Siemens Energy, Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers, Ballard Power Systems, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, Panasonic, Enapter, Proton OnSite, H-TEC Systems, Hyundai Hydrogen, Cummins Inc., Bosch, Air Liquide, and Linde |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Type (Alkaline Electrolyzers, Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers, Solid Oxide Electrolyzers, Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers) By Capacity (<1 MW, 1-10 MW, 10-100 MW, >100 MW) By Operation Type (Grid-Connected, Off-Grid), By End-Users(Energy & Utilities, Oil & Gas, Chemical & Petrochemical, Industrial Manufacturing, Transportation) |
Key Electrolyzers Company Insights
Starting back in Norway, Nel ASA builds machines that make green hydrogen using water and clean power. One kind runs on alkaline tech, another uses something called PEM; both do similar jobs differently. Power plants and factories often choose these systems when linking up with wind or solar farms. Big plans are moving forward in places like Germany, Texas, and South Korea. Equipment must run nonstop, handle shifts in supply, and grow as needs change. This is not just about selling units, it ties into how regions reshape their energy paths.
Key Electrolyzers Companies:
- Nel ASA
- ITM Power
- Plug Power
- McPhy Energy
- Siemens Energy
- Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers
- Ballard Power Systems
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- Panasonic
- Enapter
- Proton OnSite
- H-TEC Systems
- Hyundai Hydrogen
- Cummins Inc.
- Bosch
- Air Liquide
- Linde
Global Electrolyzers Market Report Segmentation
By Type
- Alkaline Electrolyzers
- Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers
- Solid Oxide Electrolyzers
- Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers
By Capacity
- <1 MW
- 1-10 MW
- 10-100 MW
- >100 MW
By Operation Type
- Grid-Connected
- Off-Grid
By End-Users
- Energy & Utilities
- Oil & Gas
- Chemical & Petrochemical
- Industrial Manufacturing
- Transportation
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to common questions.
The approximate Electrolyzers Market size for the market will be USD 48.60 billion in 2033.
Key segments for the Electrolyzers Market are By Type (Alkaline Electrolyzers, Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers, Solid Oxide Electrolyzers, Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolyzers), By Capacity (<1 MW, 1-10 MW, 10-100 MW, >100 MW), By Operation Type (Grid-Connected, Off-Grid), By End-Users(Energy & Utilities, Oil & Gas, Chemical & Petrochemical, Industrial Manufacturing, Transportation).
Major Electrolyzers Market players are Nel ASA, ITM Power, Plug Power, McPhy Energy, and Siemens Energy.
The North America region is leading the Electrolyzers Market.
The Electrolyzers Market CAGR is 29.60%.
- Nel ASA
- ITM Power
- Plug Power
- McPhy Energy
- Siemens Energy
- Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers
- Ballard Power Systems
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- Panasonic
- Enapter
- Proton OnSite
- H-TEC Systems
- Hyundai Hydrogen
- Cummins Inc.
- Bosch
- Air Liquide
- Linde
Recently Published Reports
-
Dec 2024
Active Power Filter Market
Active Power Filter Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Type (Shunt Active Power Filters, Series Active Power Filter, Hybrid Active Power Filter), By Application (Harmonics Mitigation, Reactive Power Compensation, Voltage Regulation, Power Factor Correction), By Phase (Single Phase, Three Phase), By End-User Industry (Manufacturing, Healthcare, Commercial, Automotive, Oil and Gas, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 - 2031
-
Jan 2025
Electrical Transformer Market
Electrical Transformer Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Core (Closed, Shell, and Berry), By Insulation (Gas, Oil, Solid, Air, and Other), By Phase (Single, and Three), By Rating (100 MVA to 500 MVA, 501 MVA to 800 MVA, and 801 MVA to 1200 MVA), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 – 2031
-
Jan 2025
Hydraulic Piston Pumps Market
Hydraulic Piston Pumps Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Type (Axial Piston Pumps, Radial Piston Pumps), By Operating Pressure (Low Pressure, Medium Pressure, High Pressure), By Application (Construction, Mining, Agriculture, Automotive, Oil & Gas, Industrial Machinery, Others), By End-User (OEMs, Aftermarket), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 – 2031
-
Jan 2025
Laboratory Gas Generators Market
Laboratory Gas Generators Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Product (Nitrogen Gas Generator, Hydrogen Gas Generator, Zero Air Gas Generator, Purge Gas Generator, TOC Gas Generators, Others), By Application (Gas Chromatography, Liquid Chromatography-mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), Gas Analyzers, Others), By End-user (Life Science, Chemical & Petrochemical, Food & Beverage, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 – 2031


