Market Summary
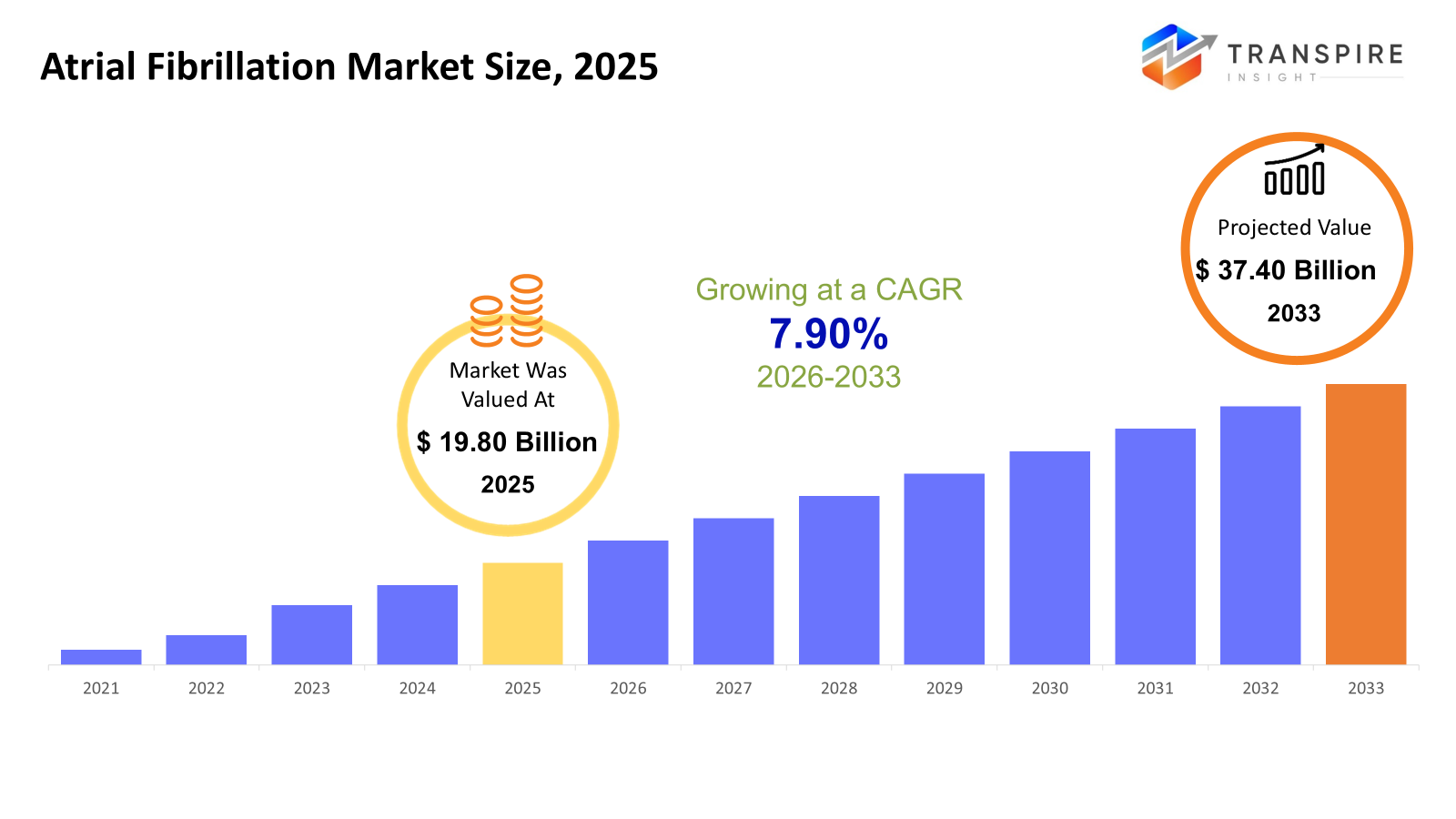
The global Atrial Fibrillation market size was valued at USD 19.80 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 37.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.90% from 2026 to 2033. More people around the world are living longer, which plays a part in why heart rhythm problems like atrial fibrillation are becoming more common. Poor diet, lack of movement, and higher blood pressure; these habits pile up, adding to the strain on hearts over time. New medicines that prevent clots now offer alternatives to older drugs, bringing change to how doctors manage risks. Tools that fix faulty heart signals through small tubes threaded into veins have gotten sharper, quicker, and less invasive. Patients recover faster, and hospitals see fewer complications.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 19.80 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 37.40 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 7.90%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- The North American market share is estimated to be approximately 41% in 2026. North America
- Medicines team up with cutting-edge methods to push expansion forward. Solid hospital networks help speed things up across the region. Places where care gets used a lot end up claiming the biggest slice simply by staying active. Growth sticks around where systems work well.
- The United States strong rise in medication use drives this area forward, fueled by widespread atrial fibrillation plus quick uptake of fresh treatments.
- Around the Asia Pacific, medicine-based treatment takes the lead. Fastest growth worldwide shows up here, driven by a better understanding plus more spending on health care
- Permanent Atrial Fibrillation shares approximately 49% in 2026. Persistent fluttering of the heart holds the top spot; its long-term course keeps patients returning. Medical visits pile up simply because it never goes away.
- Medicine takes the lead, growing quickest among options because doctors often start with rhythm-control drugs alongside blood thinners. Though methods differ, pills remain central due to their immediate role in managing irregular heartbeats.
- What stands out about cryoablation is not just how fast it is growing, but the fact that doctors are choosing it more often during atrial fibrillation treatments. Safety seems to play a big role in its growing popularity. New numbers keep showing up, each one pointing toward wider use.
- Most hospital beds fill first, due to strong systems inside, plus steady patient flow, along with full treatment paths.
A heartbeat that skips its usual pattern brings many options into play: ways to treat, tools to track, paths for ongoing care. Shaped heavily by how long people live with it, the condition pushes systems to keep watch over time, stick to medicines, and see doctors now and then. Instead of just fixing moments when things go wrong, attention now spreads wider: steady rhythms, controlled speed, blocking strokes all woven together. This shift keeps both pills and devices in regular use, pulled forward by real needs on the ground.
Medicines still play a key part in handling atrial fibrillation, especially blood thinners along with rhythm-stabilizing drugs meant to lower risks while supporting daily living. New versions of these pills, better safety records, plus easier routines for taking them have made pharmaceuticals more trusted right from the start. Meanwhile, options beyond drugs like targeted tissue treatments or electric reset procedures are seeing wider use when medications fail or when steady heart patterns matter most over the years.
What's happening in tech is changing how tools work, particularly those used to treat heart rhythm issues, map electrical activity, and track health signs. With live data processing now built into wearables and distant tracking setups, spotting problems early becomes easier, along with keeping care going over time. Because of these shifts, doctors can adjust treatments based on individual needs, guiding choices during every phase of irregular heartbeat conditions.
A growing number of clinics now rely on remote tracking instead of frequent office visits. Care plans often start with spotting risks before symptoms appear, then build from there through clear guidance for patients. This move away from reactive steps comes alongside stronger attention to avoiding hospital stays. New patterns in treatment show how digital tools fit into daily routines, helping keep outcomes steady over time. Shifts like these quietly reshape how irregular heart rhythms are managed outside intensive settings.
Atrial Fibrillation Market Segmentation
By Type of Atrial Fibrillation
- Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
Episodes of irregular heartbeat come and go on their own. Treatment usually begins with medication. What sets this type apart is how it disappears without intervention, though symptoms can return unpredictably. Medicines help control the rhythm, sometimes preventing future flare-ups. The heart resets itself, yet monitoring stays important over time.
- Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Pacing back beyond a week, atrial fibrillation sticks around without fading on its own. Doctors often step in either with meds or shocks to reset the heartbeat's pattern. Rhythm correction does not happen naturally once it drags past seven days.
- Permanent Atrial Fibrillation
Pacing is not tried anymore when someone has permanent atrial fibrillation; efforts shift straight to slowing the heartbeat while cutting stroke risk. Staying steady matters more than fixing the pattern once it settles into this ongoing state.
- Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
That’s how long atrial fibrillation lasts in this form. Treatment often shifts toward devices or specialized procedures instead of pills. Lasting this long usually means the heart rhythm problem has settled in deeply.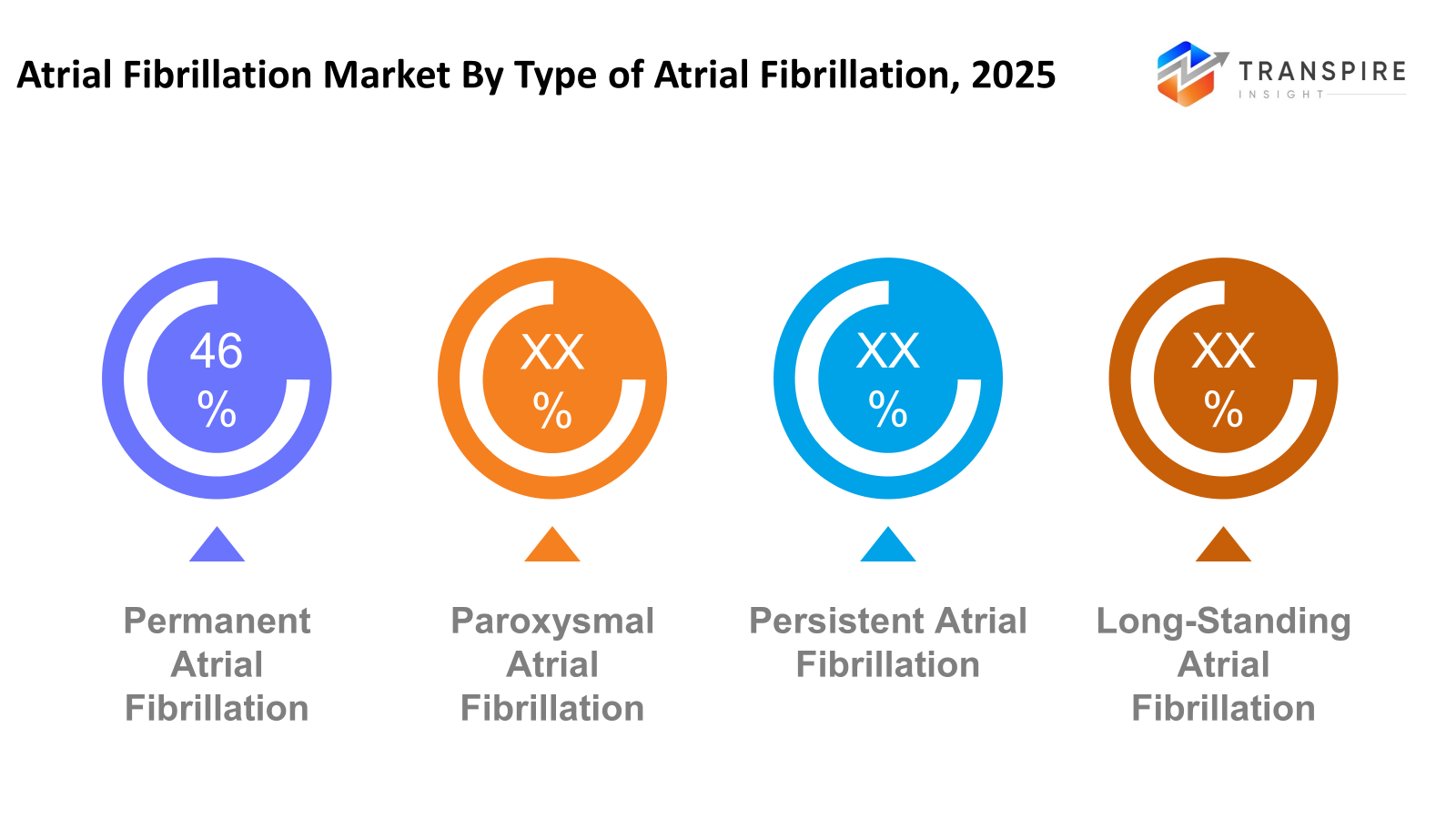
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Treatment
- Pharmacological Treatment
Medicines help manage irregular heartbeat while lowering the chances of stroke. Some drugs steady the pulse; others prevent clots from forming. Rhythm control comes through specific medications, whereas blood thinners handle clot risks. Different types work in separate ways; one keeps timing stable, another stops blockages. Treatment uses one approach for beat regulation, a different one for circulation safety.
- Non-Pharmacological Treatment
Catheter ablation might fix irregular rhythms by targeting problem areas inside the heart. Sometimes doctors choose cardioversion, using controlled shocks to reset the heartbeat's pattern. Surgery enters the picture when other methods fall short, reshaping how the electrical signals move. Each approach skips medication entirely, focusing instead on physical changes that guide a steadier pulse.
By Technology
- Radiofrequency Ablation
A zap of radio waves heats heart spots that cause irregular beats. This method wipes out faulty circuits inside the heart. Most clinics rely on it when fixing rhythm problems. Heat energy does the work by shutting down trouble zones. It remains the go-to choice across hospitals worldwide.
- Cryoablation
Frozen energy cuts off lung vein signals, shortening surgery time while holding results steady. A cold approach keeps recovery predictable without stretching the clock.
- Laser Ablation
A burst of laser light cuts tiny areas of heart tissue, used mostly by hospitals that focus on complex rhythm treatments.
- Monitoring Devices
A heartbeat tracker might be a small gadget you wear. Some slip under the skin, others stay outside like watches. These tools catch irregular rhythms when they happen. One type records heartbeats nonstop for days. Another grabs data only when symptoms show up. Each device sends info to doctors through wireless links. What matters most is spotting atrial fibrillation early, before problems grow.
- Others
A few extras slip in, things like new gadgets or helper tools, tagged onto main rhythm fixes. These bits are not central, just along for the ride when sorting out heartbeat hiccups.
By End-Users
- Hospitals
Few places match hospitals when it comes to handling complex heart rhythm cases. Advanced tools sit ready inside their labs, waiting. Experts trained in the electrical activity of the heart work regular shifts there. Operations requiring precision happen daily across these centers. Infrastructure built for delicate procedures gives them an edge that others lack.
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Fueled by a rise in same-day treatments, clinics that perform minor surgeries on feet are expanding fast. Outpatient care gains ground when patients skip overnight stays, thanks to less invasive techniques. Procedures that once needed hospital beds now happen in free-standing spots, driven by quicker recovery times. These centers thrive where speed meets simplicity, drawing demand away from traditional operating rooms.
- Home Care
Hospital beds shift into living rooms as monitors beep through Wi-Fi signals. Telecardiology threads heart data across towns without ambulances involved.
- Others
Some of these are specialized heart clinics, along with testing facilities, while others belong to scientific study groups.
Regional Insights
Right now, North America holds the top spot worldwide because advanced tools for diagnosis and therapy are common there. Healthcare works well across the region, which helps people get treatments, both drug-based and others, more easily. What pushes the United States ahead is its heavy role in medical studies, solid insurance backing, and quick uptake of new methods to handle atrial fibrillation. Over in Canada, progress comes from an emphasis on stopping heart issues before they start, along with access to expert heart care. Europe isn’t far behind, landing in second place thanks to older citizen groups needing more rhythm-related treatment. Clear medical rules guide practice there, and spending on irregular heartbeat solutions keeps rising. Still, how fast each country adopts these approaches varies due to different health setups within Europe.
Outpacing many regions, the Asia Pacific sees more cases of atrial fibrillation as clinics upgrade and lifestyles shift. With cities modernizing fast, heart issues climb doctors now spot them sooner than before. Japan pushes new tools for tracking irregular rhythms at home. India builds labs that map electrical signals in hearts with growing precision. In China, hospitals adopt high-end gear once rare outside major urban centers. South Korea links care networks so data flows between specialists without delay. More people get screened - not because campaigns shout louder but because systems finally reach farther. Policies now cover procedures that were out of reach just years ago. Insurance expansions mean treatment is not stalled by cost as often as it was. Clinics adapt not overnight but step by step. Devices evolve quietly alongside drugs refined through real-world use. Growth hides not in headlines but in daily shifts across thousands of visits. Each country moves differently; one speeds ahead while another tests cautiously. Still, momentum builds where access widens, and knowledge spreads beyond big cities. What grows here stems less from sudden leaps and more from persistent small gains.
Health systems in Latin America and parts of the Middle East and Africa are slowly gaining ground as more people learn about heart rhythm issues like atrial fibrillation. Instead of broad coverage, many areas rely on private clinics that offer heart care, especially where public services still face funding gaps. Even so, progress shows in cities where new hospitals open and training for doctors improves. While equipment access varies, efforts to catch heart problems early help push change forward. Some countries invest more in medical hubs focused only on heart disease, which supports better tracking and follow-up. Growth happens unevenly, yet signs point upward when urban centers lead with stronger planning and resources.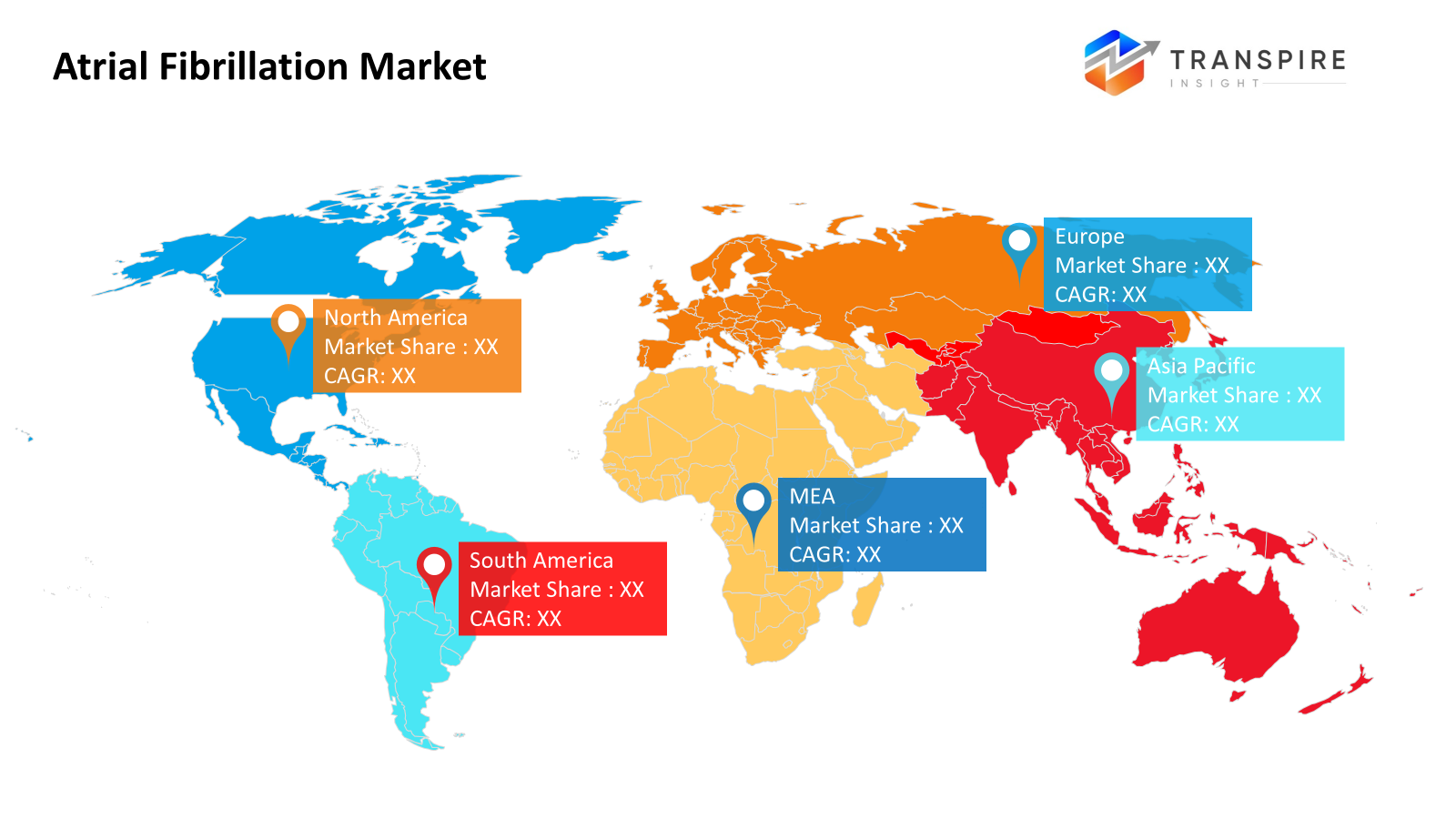
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- May 22, 2025 – Abbott launched the TactiFlex Sensor-enabled ablation catheter for a fibrillation treatment
- August 24, 2023 – GE HealthCare Launches CardioVisio for Atrial Fibrillation, a Digital, Patient-Centric Clinical Decision Support Tool to Enable Precision Care.
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 19.80 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 22.00 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 37.40 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 7.90% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
Abbott Laboratories, Medtronic plc, Boston Scientific Corporation, Johnson & Johnson (including Biosense Webster), Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Bayer AG, Pfizer Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim, AtriCure Inc., CardioFocus Inc., Biotronik SE & Co. KG, MicroPort EP MedTech, OSYPKA AG, and Synaptic Medical |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Type of Atrial Fibrillation (Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation, Persistent Atrial Fibrillation, Permanent Atrial Fibrillation, Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation), By Treatment (Pharmacological Treatment, Non-Pharmacological Treatment), By Technology (Radiofrequency Ablation, Cryoablation, Laser Ablation, Monitoring Devices, Others), By End-Users (Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Home Care, Others), |
Key Atrial Fibrillation Company Insights
A big name in global health care, Abbott Laboratories stands out in treating irregular heartbeats, especially atrial fibrillation. Instead of just stacking products, it builds smart solutions like the Volt™ Pulsed Field Ablation System, which uses focused pulses to make treatments quicker and healing smoother. Not stuck on one idea, the team added tools like the TactiFlex™ Sensor Enabled™ Ablation Catheter, helping doctors see better and act with greater control during surgery. While some companies rest, Abbott pushes ahead, testing new methods, refining gear, always aiming at real results for patients and those who treat them.
Key Atrial Fibrillation Companies:
- Abbott Laboratories
- Medtronic plc
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- Johnson & Johnson (including Biosense Webster)
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Sanofi
- Bayer AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- AtriCure Inc.
- CardioFocus Inc.
- Biotronik SE & Co. KG
- MicroPort EP MedTech
- OSYPKA AG
- Synaptic Medical
Global Atrial Fibrillation Market Report Segmentation
By Type of Atrial Fibrillation
- Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
- Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- Permanent Atrial Fibrillation
- Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
By Treatment
- Pharmacological Treatment
- Non-Pharmacological Treatment
By Technology
- Radiofrequency Ablation
- Cryoablation
- Laser Ablation
- Monitoring Devices
- Others
By End-Users
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Home Care
- Others
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa












.jpg)









 APAC:+91 7666513636
APAC:+91 7666513636





