Market Summary
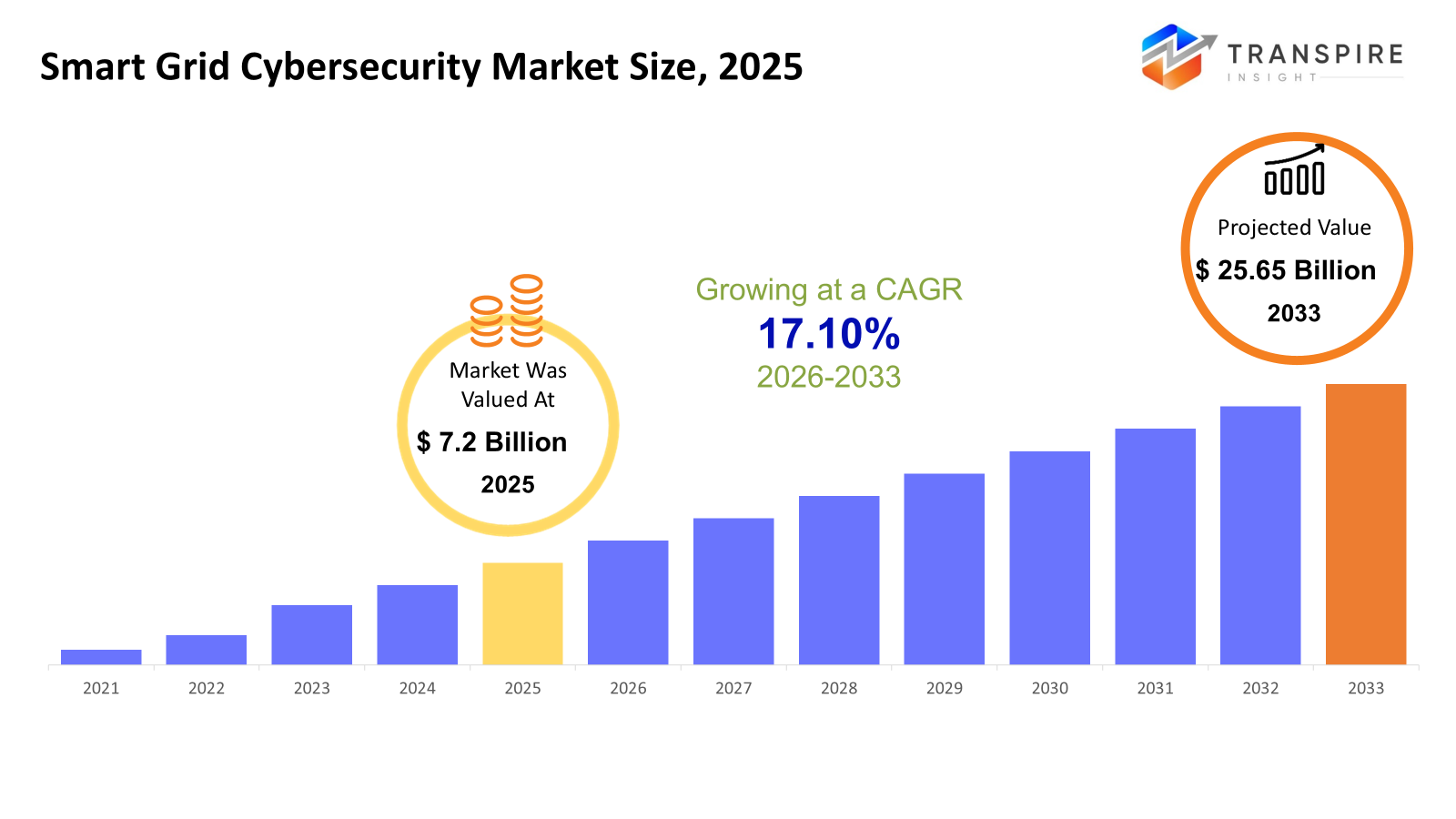
The global Smart Grid Cybersecurity market size was valued at USD 7.2 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 25.65 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 17.10% from 2026 to 2033. Increasing digitization of energy systems and integration of IoT across utilities and industrial sectors drive market CAGR growth, as these factors increase cybersecurity risks and call for more investment in protective solutions. Increasing utilization of cloud-based energy management platforms and AI-enabled analytics accelerates demand for advanced security, which fuels the growth prospectus of the market. Government regulations and compliance mandates for protecting energy infrastructure encourage continuous deployment of cybersecurity solutions, thereby contributing to the market growth. Increased critical infrastructure cyberattacks bring into perspective the growing importance of multilayered, automated, and intelligent systems for security, pushing CAGR continuously during the forecast period.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2025 Market Size: USD 7.2 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 25.65 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2033): 17.10%
- North America: Largest Market in 2026
- Asia Pacific: Fastest Growing Market
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Trends Analysis
- North America is a leading smart grid cybersecurity node, as adoption is high in utilities, BFSI, and IT sectors, adequately supported by strong regulatory frameworks, advanced infrastructure, and growing integration of smart, AI-powered cybersecurity solutions.
- The United States leads the North American region, where heavy deployments of endpoint, network, and application security solutions are witnessed within smart grid environments due to huge investments in critical infrastructure protection and massive adoption of unified threat management and SIEM platforms.
- The Asia Pacific exhibits rapid growth, with major investments expected to take place in China, Japan, India, and South Korea, as governments are focused on modernizing energy networks through renewable energy projects and the integration of AI-driven cybersecurity platforms to secure large-scale smart grids.
- Indeed, software solutions are trending as real-time threat detection, predictive analytics, and AI/ML-enabled security platforms are state-of-the-art and will enable utilities to monitor, analyze, and respond to emerging threats in a proactive way.
- Endpoint and network security are some of the top security types, providing imminent protection against breaches at device and communication network levels for seamless grid operations.
- The dominant solution types in the market are Unified Threat Management and SIEM & SOAR, which provide integrated threat detection and responses with unified monitoring across smart grid networks.
- Energy and utilities remain the top end-use sector since it depends much on continuous power distribution and critical infrastructure, which drives the adoption of comprehensive cybersecurity solutions.
So, The Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market is a constantly developing market that targets the prevention and protection of modern electrical grids from cyber threats. It also combines innovative and cutting-edge solutions in hardware, software, and services to provide efficient energy supply and flexibility in operations and characteristics. The factors that fuel the expansion and development of this market include the increased adoption and implementation rate of smart grids in different nations and settings across the world, increased penetration and uses of IoT and other devices, and increased cyber threats and attacks on infrastructure and institutions across the world. Rising digitalization and automation in energy infrastructure escalate the demand for software and AI-powered cybersecurity solutions, and hardware and services continue to play a critical role in the adoption of holistic security strategies. To deal with emerging threats and mitigate risks, businesses are now relying on joined-up strategies that include endpoint and application security, cloud and network security, and the latest AI/ML model and hardware security. Cybersecurity solutions ranging from UTM, IDS/IPS, and SIEM and SOAR to IAM, DLP, and DDoS protection have been incorporated across various sectors. The end-use industries in the field of information technology, telecommunications, the energy sector, the government sector, the BFSI sector, the healthcare sector, the manufacturing sector, the automotive sector, the transportation sector, and the marine sector are undergoing massive investments in the field of smart grid cybersecurity solutions. The increasing demand for energy, the rise of the concept of smart cities, and the inclusion of renewable sources of energy are catalyzing the integration of highly advanced cybersecurity solutions. The growth in the market is directly associated with the inclusion of the concept of connected infrastructure.
Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market Segmentation
By Component
- Hardware
Refers to firewalls, secure gateways, and sensors that safeguard the physical infrastructure of the smart grid. Critical, since flaws in infrastructure can result in attacks across the entire system.
- Software
This includes the use of monitoring tools, analytics, and security apps. Very essential for threat detection, automated response, and system integrity.
- Services
Professional services including consulting, managed security, and integration. Services are offered for expertise in implementation and ongoing risk management in complex smart grid networks.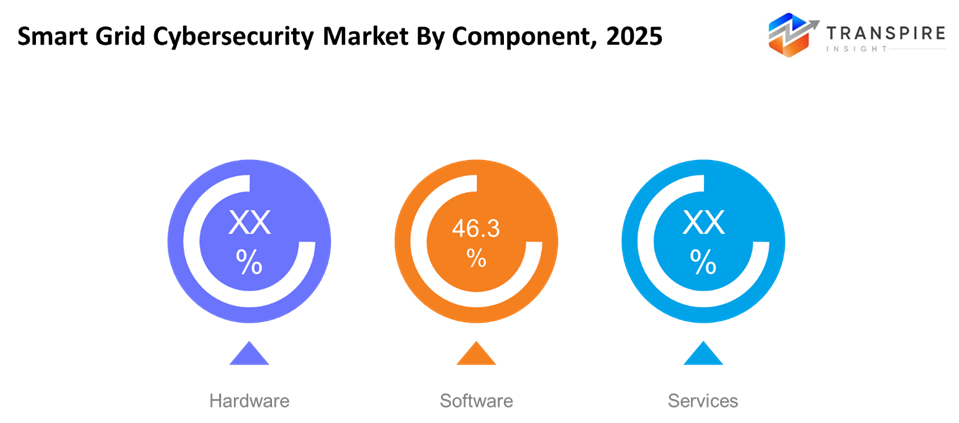
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
By Security Type
- Endpoint Security
A key component for a smart grid is endpoint security. This is because a smart grid consists of smart meters, sensors, intelligent electronic devices, as well as IoT-enabled components, most of which are located near the edge of the grid, making endpoint security a crucial component for a smart grid to prevent the entry of malware.
- Cloud Security
This has become vital with the growing need for utilities companies to move data storage, analytics, and energy management solutions onto cloud-based platforms. It enables safe data transfer, management, and compliance with regulatory processes while facilitating scalability, remote monitoring, and real-time controls in smart grid networks.
- Network Security
It provides the backbone of smart grid protection by securing the communication networks that interconnect the distribution stations, control centers, or distributed resources. This protects the smart grid from intrusion, manipulation, or denial of service attacks.
- Application Security
Application security safeguards key software systems in areas such as SCADA systems, energy resource control systems, or grid control systems against cyber threats. Application security can ensure data tampering, shutdowns, or failure does not occur in utilities as they increasingly depend on automated systems to manage their grid operations.
- Infrastructure Protection
Infrastructure protection mainly revolves around the prevention of attacks on the physical and cybersecurity domains of substation protection, power plant protection, and transmission protection, among others, to avoid sabotage, physical component damage, and mass power outages in the market.
- Data Security
Data security is a crucial element in protecting consumer usage information and billing information related to the operation of smart grids. It can be guaranteed through encryption and access control. Through data security, consumer confidence can be gained in digitalized energy infrastructure.
- AI/ML Model Security
Security in AI and machine learning models: This is an emerging market, which deals with the security of predictive analytics and automation systems, which are utilized in terms of load forecasting, fault detection, and energy optimization.
- Hardware Security
Hardware security helps to ensure that embedded systems, programmable logic controllers, and communication equipment are not vulnerable to hacking or modification. Secure hardware solutions can limit vulnerabilities at a very basic level regarding overall operational reliability within a smart grid system.
- Others
This category includes the rising security domain of blockchain security, identity verification, and quantum-resistant encryption. These technologies respond to the ever-changing nature of threat types, showing the level of innovation that is needed in the next-generation smart grid infrastructure.
By Solution Type
- Unified Threat Management (UTM)
Unified Threat Management solutions are also used to a great extent in the environment of smart grids because UTM solutions provide multiple functions, including firewall, intrusion prevention and antivirus solutions, and traffic monitoring in a single environment, which offers simplicity in managing different solutions and comprehensive protection to the grid environment.
- Intrusion Detection System / Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS)
IDS & IPS systems are considered crucial in the identification and prevention of malicious activity in smart grid communications. This is due to the systems being capable of monitoring activity in the network thereby providing early warning systems of potential disruptions of the operations of the systems.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention is a solution that protects critical operational and consumer data created as a result of smart grid deployments. Data Loss Prevention helps ensure that data is not compromised due to misuse and ensures that data is handled according to regulations.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM)
The IAM solutions provided ensure that only trusted users, devices and applications are able to access key smart grid systems. The use of secure authentication, role-based access and privilege management capabilities within IAM solutions limits the risks associated with insider threats as well as unauthorized changes that may affect the stability of the grid.
- Security Information And Event Management (SIEM) And Security Orchestration, Automation, And Response (SOAR)
SIEM and SOAR tools give utility companies centralized views into various security related events within IT and OT environments. Such tools can greatly aid utilities in improved threat analyses and automated response capabilities related to cybersecurity threats.
- DDoS Protection
Smart grid communication network protection systems defend against traffic attacks which have the capability to flood the system and affect the operation of the network. Network availability plays a crucial role in the uninterrupted supply of power and the monitoring of the grid in real time.
- Risk and Compliance Management
Risk and Compliance Management Solutions enable utilities to evaluate their vulnerabilities against cyber threats and apply effective mitigation strategies. Risk and Compliance Management Solutions enable utilities to implement industry and government standards for secure operations.
- Others
The other types of solutions include the following: Zero trust security frameworks, blockchain security, threat intelligence systems, and anomaly detection solutions that employ the use of artificial intelligence.
By End Use
- IT and Telecommunications
IT, telecommunication companies, and other organizations utilize the application of smart grid cybersecurity in order to safeguard the communication network, data transfer, and the integrated digital infrastructure. With the rise in the usage of data in the power sector, the availability of the network should be secured.
- Retail and E-Commerce
The retail and online business industry uses smart grid cybersecurity to protect data related to electricity consumption, online payment systems, and the billing infrastructure. Secure electricity infrastructure protects against data breaches, business continuity, and data protection regulation compliance.
- BFSI
In the BFSI industry, the protection of financial transactions, billing, and critical data of customers associated with energy consumption is addressed through the use of smart grid cybersecurity solutions. Better cybersecurity solutions can thus abate the risks of fraud associated with these systems.
- Healthcare
Healthcare facilities require reliable smart grid infrastructure to provide them with uninterrupted power supplies for their critical equipment such as data centers. Cybersecurity solutions for smart grids eliminate any risks associated with power outages, as well as protecting patient information.
- Government and Defense
- Smart grid security solutions are of utmost importance to both the government and defense institutions to shield their country's electricity grid system from cyber espionage, sabotage, and terrorism. These solutions enhance energy security and adhere to strict national security policies.
- Manufacturing
The manufacturing plants use the concept of smart grid cybersecurity to shield their highly energy-demanding production units. The OT cybersecurity of the factories prevents the occurrence of breakdowns, lost production, and cyber-threat-related downtimes in industrial operations.
- Energy and Utilities
The energy and utilities business is the most extensive business in the end use market, given the fact that they have critical infrastructure that needs constant, uninterrupted power distribution. Cybersecurity solutions for the smart grid protect substations, managing systems, and distributed energy resources.
- Automotive
Smart grids' cybersecurity in the automotive industry is applied in securing electric car charging infrastructure and smart mobility. Their security is important for securing the integration of electric vehicles, preventing any services from being interrupted.
- Marine
The marine and port sectors depend on the use of smart grid cybersecurity systems to ensure the functionality of the powering systems necessary for navigation, logistics, and marine infrastructure.
- Transportation & Logistics
The transportation and logistics industry relies on a secure smart grid infrastructure for energy provisioning for rail transport, traffic control systems, and logistic facilities. Cyber security solutions enable free and uninterrupted operations as well as efficient supply chain management.
- Others
The other user markets include Smart Cities, Educational Institutions, as well as critical infrastructure facilities. The increasing digitalization of energy in such markets creates a demand for custom solutions in Smart Grid Cyber Security.
Regional Insights
The Smart Grid CybersecurityMarket in the global arena covers several major regions with unique drivers. The key region of North America, with a focus on the US, leads in cutting-edge smart grid systems as well as tough government guidelines. The other nations, namely Canada and Mexico, are following suit in critical infrastructure spending. The key countries in the European arena with high demands are German, UK, France, Spanish, and Italian. The utilities industry in this region follows AI-based cybersecurity systems. The Asia Pacific market, mainly consisting of Japanese, Chinese, Indian, Korean, and Australia & New Zealand, witnesses a steep growth trajectory with advancements in modernized smart grid systems. The South American region, which involves Brazilian & Argentinean countries, witnesses a steady acceptance of modernized smart grid systems with a growing emphasis on cybersecurity infrastructure. The regions in Middle East & Africa, mainly consisting of Saudi Arabian, UAE, as well as South African countries, are making significant investments in a strong energy infrastructure to fuel their economy. The Tier 1 sub-regions in most nations tend to be technology leaders initially, with Tier 2 sub-regions following suit. Thus, overall, this market witnesses a geographical expansion.
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample Report
Recent Development News
- December 2025, erviceNow made a $7.75 billion acquisition of cybersecurity company Armis to enhance the security offerings which will focus on AI and OT. Such a move clearly indicates a focus on the security of intelligent environments, like the smart grid and critical infrastructures.
- In October 2025, Svenska kraftnät, the Swedish transmission system operator responsible for the entire Swedish electricity grid, reported that it was hit by a ransomware attack and data breach. It was documented that there was no impact on the critical operational infrastructure.
(Source:https://www.techradar.com/pro/security/sweden-power-grid-confirms-cyberattack-ransomware-suspected)
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 7.2 Billion |
|
Market size value in 2026 |
USD 8.5 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 25.65 Billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 17.10% from 2026 to 2033 |
|
Base year |
2025 |
|
Historical data |
2021 – 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2026 – 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
United States; Canada; Mexico; United Kingdom; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; China; Japan; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; South Africa; Saudi Arabia; United Arab Emirates |
|
Key company profiled |
IBM Corporation, Siemens AG, Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, Honeywell International Inc., General Electric Company (GE), BAE Systems plc, Fortinet, Inc., Palo Alto Networks, Inc., ABB Ltd., Lockheed Martin Corporation, Trend Micro, Inc., CyberArk Software Ltd., Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., AlienVault Inc. |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (country, regional & segment scope). Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. |
|
Report Segmentation |
By Security Type (Hardware, Software, Services), By Security Type (Endpoint Security, Cloud Security, Network Security, Application Security, Infrastructure Protection, Data Security, Artificial Intelligence Model/Machine Learning Model Security, Hardware Security, Others), By Solution Type (Unified Threat Management (UTM), Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Identity and Access Management (IAM), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) & Security Orchestration, Automation & Response (SOAR), DdoS, Risk and compliance management, Others) and By End Use (IT and Telecommunications, Retail and E-Commerce, BFSI, Healthcare, Government and Defense, Manufacturing, Energy and Utilities, Automotive, Marine, Transportation and Logistics, Others) |
Key Smart Grid Cybersecurity Company Insights
IBM Corporation is a prominent player in the smart grid cybersecurity market due to its expertise in critical infrastructure protection and AI-powered threat analysis, hybrid cloud security, and analytics. The company’s cybersecurity offerings, such as IBM QRadar, provide utilities with real-time situational awareness, automated incident response, and predictive threat intelligence, which helps utilities defend proactively against threats in IT and operational domains. The strength of IBM Corporation is its ability to deliver services worldwide, with extensive research and development, and partnerships with energy companies that improve resistance to emerging threats. The company’s offerings are designed to protect distributed energy resources, advanced metering infrastructure, and grid automation systems.
Key Smart Grid Cybersecurity Companies:
- IBM Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Honeywell International Inc.
- General Electric Company (GE)
- BAE Systems plc
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- ABB Ltd.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Trend Micro, Inc.
- CyberArk Software Ltd.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- AlienVault Inc.
Global Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market Report Segmentation
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Security Type
- Endpoint Security
- Cloud Security
- Network Security
- Application Security
- Infrastructure Protection
- Data Security
- Artificial Intelligence Model/Machine Learning Model Security
- Hardware Security
- Others
By Solution Type
- Unified Threat Management (UTM)
- Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS)
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) & Security Orchestration, Automation & Response (SOAR)
- DDoS
- Risk and compliance management
- Others
By End Use
- IT and Telecommunications
- Retail and E-Commerce
- BFSI
- Healthcare
- Government and Defense
- Manufacturing
- Energy and Utilities
- Automotive
- Marine
- Transportation and Logistics
- Others
Regional Outlook
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- Australia & New Zealand
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to common questions.
The approximate Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market size for the market will be USD 25.65 billion in 2033.
Key segments for the Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market are By Security Type (Hardware, Software, Services), By Security Type (Endpoint Security, Cloud Security, Network Security, Application Security, Infrastructure Protection, Data Security, Artificial Intelligence Model/Machine Learning Model Security, Hardware Security, Others), By Solution Type (Unified Threat Management (UTM), Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Identity and Access Management (IAM), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) & Security Orchestration, Automation & Response (SOAR), DdoS, Risk and compliance management, Others) and By End Use (IT and Telecommunications, Retail and E-Commerce, BFSI, Healthcare, Government and Defense, Manufacturing, Energy and Utilities, Automotive, Marine, Transportation and Logistics, Others)
Major Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market players are IBM Corporation, Siemens AG, Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, Honeywell International Inc.
The North America region is leading the Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market.
The CAGR of the Smart Grid Cybersecurity Market is 17.10%.
- IBM Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Honeywell International Inc.
- General Electric Company (GE)
- BAE Systems plc
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- ABB Ltd.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Trend Micro, Inc.
- CyberArk Software Ltd.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- AlienVault Inc.
Recently Published Reports
-
Dec 2024
3D Optical Profiler Market
3D Optical Profiler Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Type (Desktop 3D Optical Profiler, and Portable 3D Optical Profiler), By Technology (Confocal Technology, and White Light Interference), By End-Use Industry (Manufacturing, Research Institutions, Automotive, Aerospace and Defense, Medical Devices, and Other), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 - 2031
-
Feb 2025
Depth Sensor Market
Depth Sensor Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Type (Infrared Depth Sensors, Time-of-Flight (ToF) Sensors, Stereo Vision Sensors, Structured Light Sensors, Ultrasonic Depth Sensors), By Application (Automotive, Robotics, Gaming, Consumer Electronics, Industrial Automation, Healthcare, Security & Surveillance, Others), By End Users (Automotive Manufacturers, Consumer Electronics Companies, Healthcare Providers, Industrial Companies, Security Agencies, Gaming Companies, Robotics Companies, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 – 2031
-
Feb 2025
Digital Manufacturing Market
Digital Manufacturing Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Component (Hardware, Software, and Services), By Technology (Robotics, 3D Printing, Internet of Things (IoT), and Others), By Application (Automotive and Transportation, Aerospace and Defense, Consumer Electronics, Industrial Machinery, and Others), By Process Type (Computer-Based Designing, Computer-Based Simulation, Computer 3D Visualization, Analytics, and Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 – 2031
-
Feb 2025
Digital Visa Services Market
Digital Visa Services Market Size, Share & Analysis Report By Type (Individual Travelers, Group Travelers), By Application (Tourism, Business Travel, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South and Central America), 2021 – 2031


